Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
As you use your AI models and prompts, you might have to access data to monitor their activity or consumption.
The Monitor activity section of the AI hub in the Power Automate portal provides tables that you can use to monitor AI models and prompts. You can also monitor the data that they process, and track their consumption.

View AI Builder activity
The AI Builder activity page shows AI model and prompts activity, including activity generated in Power Automate, Power Apps, and Microsoft Copilot Studio.
Learn more in What is Power Apps? and Copilot Studio overview.
Sign in to Power Automate.
On the navigation pane to the left, select AI hub.
Select Monitor activity.
(Optional) Review the activity on the page and customize the data that shows by filtering the timeframe or tool type.

By default, data displays for all AI models from the last seven days.
The following table describes the columns on the AI Builder activity page.
Column heading Description Processed time The time when processing occurs. Tool name The AI model or prompt name. Input The text input of the AI model predictaction for text processing models, or the value Image or Document for other models and prompts.Output The GPT prompt output (model response) in the selected output format. Used in The consumption source of the AI model or prompt. It can be Power Automate, Power Apps, Copilot Studio, or Quick Test for saved but not consumed prompts. Consumption The numeric consumption value for the related AI model or prompt run. When you select each event in the table, more details show.

Detail Description Processed by The name of the person who performs the predict action. This person is typically the owner of the Power Automate cloud flow or the person who runs the app created in Power Apps. Model The name of the language model used in the prompt run.
Monitor data for makers and admins
If you want to monitor the use of your AI models and prompts, the AI Builder activity section is helpful. It's also helpful for environment admins who want to monitor all activity in an environment.
Note
- The monitoring data is stored in the AI Event table in your Dataverse instance. It persists in the table even if you delete the model, cloud flow, and app.
- You're required to have Write access to this table to record AI model and prompt activity.
- The AI Event Dataverse table contains input of the AI model predict actions for text scenarios only.
The data that you can display depends on your role.
| Role | What you can display |
|---|---|
| System Administrator | All activity for all AI models. |
| System Customizer | All activity for all AI models. |
| Basic User | Only your own activity for the AI models that you have access to. |
| Environment Maker | Only your own activity for the AI models that you have access to. |
Manage AI Builder activity monitoring data
Through effective management of the historical data that your Power Automate flows, Power Apps, or other Microsoft Power Platform products generate, you ensure that your Dataverse environments remain efficient and cost-effective. By implementing data retention policies and using features such as bulk record deletion in Dataverse and Power Platform admin center, you can proactively manage the accumulation of historical data.
This section of the article explains how to identify the historical AI Builder activity monitoring data that can be purged from your environment. It then explains how to use Dataverse's built-in bulk-delete feature to purge it. With the bulk-delete feature, you can quickly and easily remove large amounts of data from your environment in a way that complies with your specific data retention policies. This approach ensures efficient data storage and performance management.
In addition to on-demand bulk-delete jobs, you can schedule recurrent bulk-delete jobs that find and delete records in a table that are, for example, older than a specified number of days (OlderThanXDays query function).
To create bulk-delete jobs in Dataverse, you must have the Bulk Delete privilege in at least one of the roles that is assigned to you.
Caution
When you delete Dataverse data, it is permanently deleted from your environment. There's no way to recover individual records after you delete them.
Export a Dataverse table
The following table shows an AI Builder activity monitoring Dataverse table that might have large data volumes.
| Display name | System name | Details |
|---|---|---|
| AI Event | Msdyn_aievent | The AI Event table stores activity data about AI model and prompt activity. This data includes the processed data type, processed data information for text scenarios, processing date, processing status, and consumption. |
As the data is stored in your AI Event Dataverse table, you can export it in comma-separated values (CSV) format. Learn how to export data in Import data from Excel and export data to CSV.
Delete AI Builder activity monitoring data
To delete AI Builder activity monitoring data, you must create a bulk-delete job. To bulk-delete data in Dataverse, follow these steps.
Caution
Bulk-delete operations are irreversible. Before you perform bulk-delete operations, thoroughly test and review your filter results.
Sign in to Power Platform admin center.
On the left navigation pane, select Environments, select your environment, and then select Settings on the top menu bar.
Select Data management > Bulk deletion.
Select New on the command bar above the All Bulk Deletion System Jobs grid. The Bulk Deletion Wizard appears, where you define a query for the records that you want to delete.
Select Next.
In the Look for list, select the AI Events table.
In the search criteria area, add the filter that should return the records that you want to delete. For example, the filter in the following screenshot finds all AI Builder model activity that is older than six months.
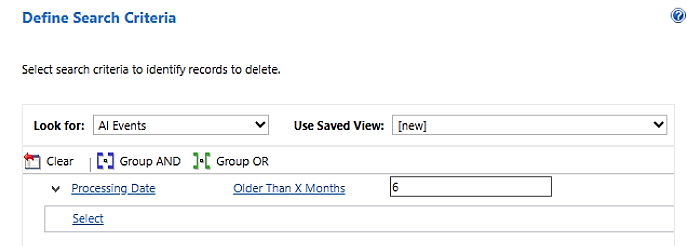
Select Next.
In the Name field, enter a name for the bulk-delete job (for example, Bulk-delete of AI models monitoring data older than 6 months).
In the At scheduled time section, select a start date and time for the job. Select a time when users aren't typically online.
Select the Run this job after every checkbox.
In the days list, select the frequency that you want the job to run at.
If you want to receive a notification email, select the Send an email to me (<your email address>) when this job is finished checkbox.
Select Next.
On the Review and Submit Bulk Deletion Details page, review the bulk-delete job.
Select Submit to create the recurring job.