Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Grounding with Bing Search allows your Azure AI Agents to incorporate real-time public web data when generating responses. You need to create a Grounding with Bing Search resource, and then connect this resource to your Azure AI Agents. When a user sends a query, Azure AI Agents decide if Grounding with Bing Search should be leveraged or not. If so, it will leverage Bing to search over public web data and return relevant chunks. Lastly, Azure AI Agents will use returned chunks to generate a response.
You can ask questions such as "what is the top news today" or "what is the recent update in the retail industry in the US?", which require real-time public data.
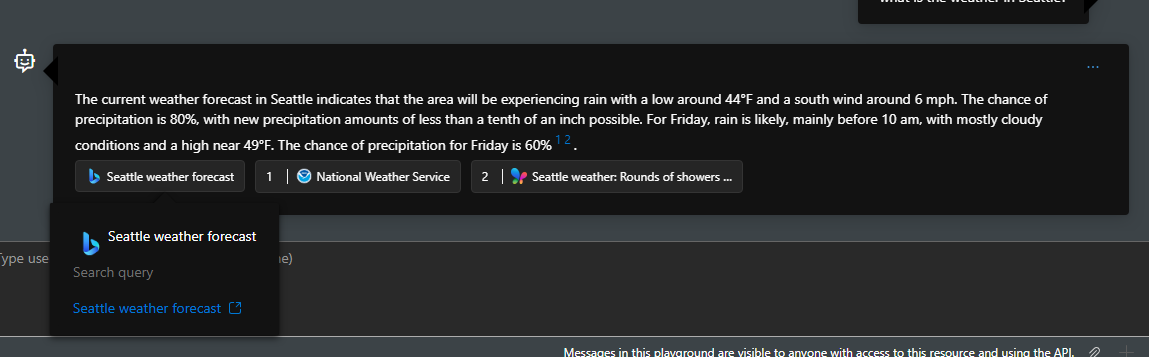
Developers and end users don't have access to raw content returned from Grounding with Bing Search. The model response, however, includes citations with links to the websites used to generate the response, and a link to the Bing query used for the search. You can retrieve the model response by accessing the data in the thread that was created. These two references must be retained and displayed in the exact form provided by Microsoft, as per Grounding with Bing Search's Use and Display Requirements. See the how to display Grounding with Bing Search results section for details.
Important
- Your usage of Grounding with Bing Search can incur costs. See the pricing page for details.
- By creating and using a Grounding with Bing Search resource through code-first experience, such as Azure CLI, or deploying through deployment template, you agree to be bound by and comply with the terms available at https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/bing/apis/grounding-legal, which may be updated from time to time.
- When you use Grounding with Bing Search, your customer data is transferred outside of the Azure compliance boundary to the Grounding with Bing Search service. Grounding with Bing Search is not subject to the same data processing terms (including ___location of processing) and does not have the same compliance standards and certifications as the Azure AI Foundry Agent Service, as described in the Grounding with Bing Search Terms of Use. It is your responsibility to assess whether use of Grounding with Bing Search in your agent meets your needs and requirements.
How Grounding with Bing Search works
The user query is the message that an end user sends to an agent, such as "should I take an umbrella with me today? I'm in Seattle." Instructions are the system message a developer can provide to share context and provide instructions to the AI model on how to use various tools or behave.
When a user sends a query, the customer's AI model deployment first processes it (using the provided instructions) to later perform a Bing search query (which is visible to developers). Grounding with Bing returns relevant search results to the customer's model deployment, which then generates the final output.
Note
When using Grounding with Bing Search, only the Bing search query, tool parameters, and your resource key are sent to Bing, and no end user-specific information is included. Your resource key is sent to Bing solely for billing and rate limiting purposes.
The authorization will happen between Grounding with Bing Search service and Azure AI Foundry Agent Service. Any Bing search query that is generated and sent to Bing for the purposes of grounding is transferred, along with the resource key, outside of the Azure compliance boundary to the Grounding with Bing Search service. Grounding with Bing Search is subject to Bing's terms and do not have the same compliance standards and certifications as the Azure AI Foundry Agent Service, as described in the Grounding with Bing Search Terms of Use. It is your responsibility to assess whether the use of Grounding with Bing Search in your agent meets your needs and requirements.
Transactions with your Grounding with Bing resource are counted by the number of tool calls per run. You can see how many tool calls are made from the run step.
Supported capabilities and known issues
- Grounding with Bing Search tool is designed to retrieve real-time information from web, NOT specific web domains.
- NOT Recommended to summarize an entire web page.
- Within one run, the AI model will evaluate the tool outputs and may decide to invoke the tool again for more information and context. AI model may also decide which piece(s) of tool outputs are used to generate the response.
- Azure AI Agent service will return AI model generated response as output so end-to-end latency will be impacted pre-/post-processing of LLMs.
- Grounding with Bing Search tool does NOT return the tool output to developers and end users.
Usage support
| Azure AI foundry support | Python SDK | C# SDK | JavaScript SDK | Java SDK | REST API | Basic agent setup | Standard agent setup |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
Setup
Note
- Grounding with Bing Search works with all Azure OpenAI models that Azure AI Foundry Agent Service supports, except
gpt-4o-mini, 2024-07-18.
Create an Azure AI Agent by following the steps in the quickstart.
Create a Grounding with Bing Search resource. You need to have
ownerorcontributorrole in your subscription or resource group to create it.- You can create one in the Azure portal, and select the different fields in the creation form. Make sure you create this Grounding with Bing Search resource in the same resource group as your Azure AI Agent, AI Project, and other resources.
- You can also create one through code-first experience. If so, you need to manually register Bing Search as an Azure resource provider. You must have permission to perform the
/register/actionoperation for the resource provider. The permission is included in the Contributor and Owner roles.
az provider register --namespace 'Microsoft.Bing'After you have created a Grounding with Bing Search resource, you can find it in Azure portal. Navigate to the resource group you've created the resource in, search for the Grounding with Bing Search resource you have created.
Optional parameters
When you add the Grounding with Bing Search tool to your agent, you can pass the following parameters. These parameters will impact the Grounding with Bing Search tool output, and the AI model might not fully use all of the outputs. See the code examples for information on API version support and how to pass these parameters.
| Name | Value | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
count |
The number of search results to return in the response. The default is 5 and the maximum value is 50. The actual number delivered may be less than requested. It is possible for multiple pages to include some overlap in results. This parameter affects only web page results. It's possible that AI model might not use all search results returned by Bing. | UnsignedShort |
No |
freshness |
Filter search results by the following case-insensitive age values: Day: Return webpages that Bing discovered within the last 24 hours. Week: Return webpages that Bing discovered within the last 7 days. Month: Return webpages that Bing discovered within the last 30 days. To get articles discovered by Bing during a specific timeframe, specify a date range in the form: YYYY-MM-DD..YYYY-MM-DD. For example, freshness=2019-02-01..2019-05-30. To limit the results to a single date, set this parameter to a specific date. For example, freshness=2019-02-04. |
String | No |
market |
The market where the results come from. Typically, mkt is the country where the user is making the request from. However, it could be a different country if the user is not located in a country where Bing delivers results. The market must be in the form: <language>-<country/region>. For example, en-US. The string is case insensitive. For a list of possible market values, see Market codes. If known, you are encouraged to always specify the market. Specifying the market helps Bing route the request and return an appropriate and optimal response. If you specify a market that is not listed in Market codes, Bing uses a best fit market code based on an internal mapping that is subject to change. |
String | No |
set_lang |
The language to use for user interface strings. You may specify the language using either a 2-letter or 4-letter code. Using 4-letter codes is preferred. For a list of supported language codes, see Bing supported languages. Bing loads the localized strings if setlang contains a valid 2-letter neutral culture code (fr) or a valid 4-letter specific culture code (fr-ca). For example, for fr-ca, Bing loads the fr neutral culture code strings.If setlang is not valid (for example, zh) or Bing doesn’t support the language (for example, af, af-na), Bing defaults to en (English).To specify the 2-letter code, set this parameter to an ISO 639-1 language code. To specify the 4-letter code, use the form <language>-<country/region> where <language> is an ISO 639-1 language code (neutral culture) and <country/region> is an ISO 3166 country/region (specific culture) code. For example, use en-US for United States English.Although optional, you should always specify the language. Typically, you set setLang to the same language specified by mkt unless the user wants the user interface strings displayed in a different language. |
String | No |
How to display Grounding with Bing Search results
According to Grounding with Bing's terms of use and use and display requirements, you need to display both website URLs and Bing search query URLs in your custom interface. You can find website URLs through annotations parameter in API response and Bing search query URLs through runstep details. To render the webpage, we recommend you replace the endpoint of Bing search query URLs with www.bing.com and your Bing search query URL would look like "https://www.bing.com/search?q={search query}"
run_steps = project_client.agents.runs_steps.list(run_id=run.id, thread_id=thread.id)
run_steps_data = run_steps['data']
print(f"Last run step detail: {run_steps_data}")
Next steps
See code samples for using the Grounding with Bing tool programmatically.