Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
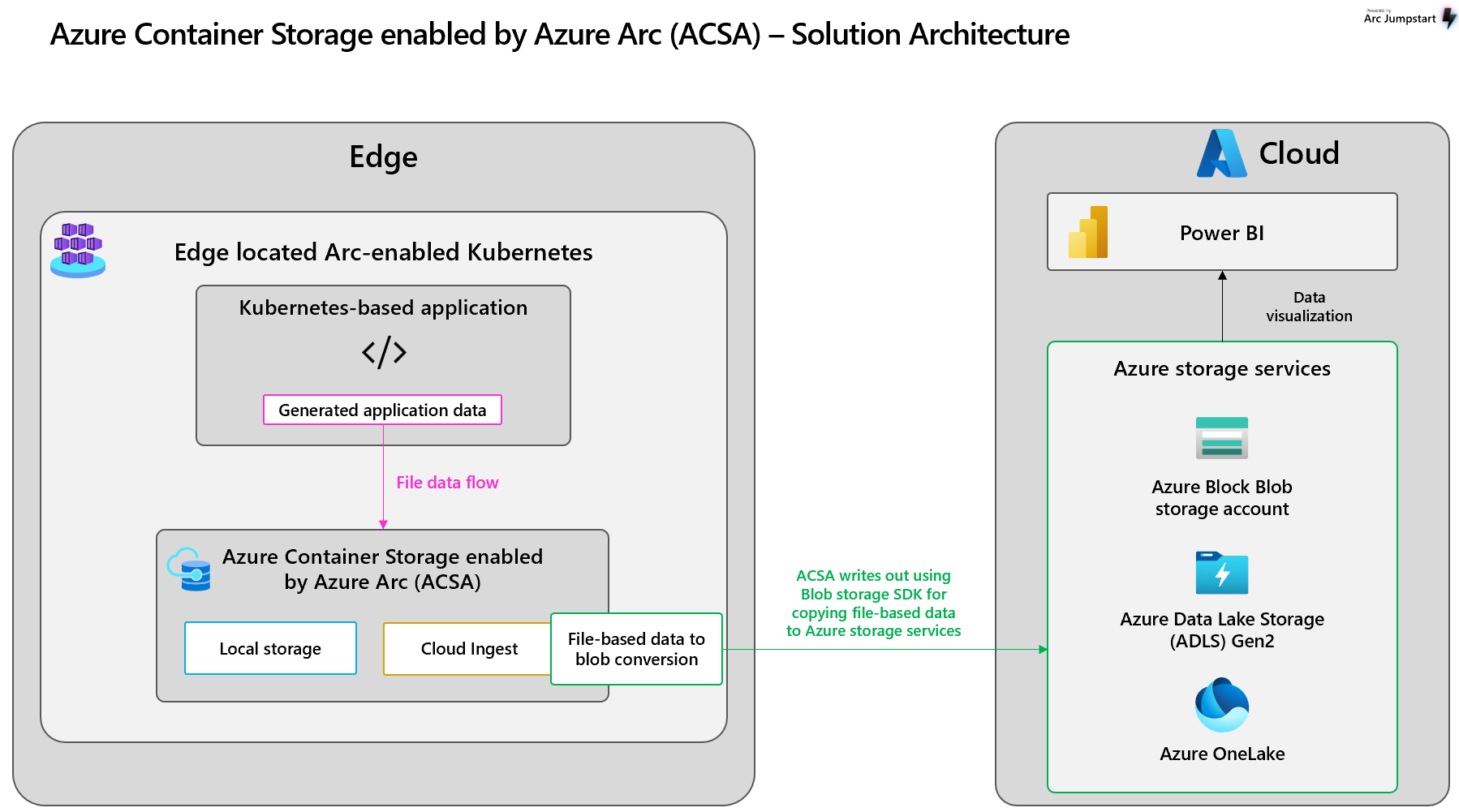
Azure Container Storage enabled by Azure Arc is a first-party storage system designed for Arc-connected Kubernetes clusters. This Arc extension can be deployed to write files to a ReadWriteMany persistent volume claim (PVC) where they can be stored locally, transferred to Azure Blob Storage destinations in the cloud, or mirrored from those cloud destinations.
Azure Container Storage offers a range of features to support various workloads, such as AI and ML training models, Azure IoT Operations, and other Arc services. With high availability and fault-tolerance options available, this Arc extension is ready for production workloads.
To download architecture diagrams in high resolution, visit Jumpstart Gems.
What does Azure Container Storage do?
Azure Container Storage serves as a native persistent storage system for Arc-connected Kubernetes clusters. Its primary role is to provide a flexible, reliable, fault-tolerant file system that allows data to be kept safely at the edge, to be tiered to Azure, or to be mirrored from the cloud and available locally.
Key features of Arc-connected clusters running this extension include:
- Tolerance to node failures: When configured as a three or more node clusters, Azure Container Storage replicates data between nodes to ensure high availability and tolerance to single node failures.
- Storage Local to your cluster: With a Local Shared Edge Volume, the user can store data local to their edge deployment with a ReadWriteMany access model.
- Data synchronization to Azure: Azure Container Storage is configured with a storage target, so data written to volumes is automatically tiered to Azure Blob (block blob, Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2, or OneLake) in the cloud.
- Data mirror from Azure (preview): Azure Container Storage is configured with a storage target, so data written to that storage destination is automatically mirrored as a Read Only copy to the local volume in your cluster.
- Simple connection: Customers can easily connect to a configured volume using a CSI driver to start making persistent volume claims against their storage.
- Observable: Supports industry standard Kubernetes monitoring logs and metrics facilities, and supports Azure Monitor Agent observability.
What are the Azure Container Storage offerings available?
Local Shared Volumes: Provides highly available, failover-capable storage, local to your Kubernetes cluster. This shared storage type remains independent of cloud infrastructure, making it ideal for scratch space, temporary storage, and locally persistent data unsuitable for cloud destinations.
Cloud Ingest subvolumes: Facilitates limitless data ingestion from edge to Blob, including Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 and OneLake. Files written to this storage type are seamlessly transferred to Blob storage and then purged from the local cache once confirmed uploaded, ensuring space availability for new data. Configurable policies allow for flexibility in upload and purge behaviors. Moreover, this storage option supports data integrity in disconnected environments, enabling local storage and synchronization upon reconnection to the network.
Cloud Mirror subvolumes (preview): Mirror data from the cloud to the edge. Using cloud blob storage as the data origin, Mirror subvolumes allow content distribution from the cloud to edge located Kubernetes applications. The cloud copy of your data is still the authoritative version, so your local copy is a mirror image of that blob container's data. A Mirror subvolume provides your application with a ReadOnly file system replica for reference at the edge. The Mirror subvolume is ReadOnly and data can't be modified or deleted by workloads consuming the data at the edge. If you'd like to change the data, you must edit the authoritative cloud version.
Detailed Architecture
To download architecture diagrams in high resolution, visit Jumpstart Gems.