Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This article details how to use an Azure Resource Manager (ARM) template in the Azure portal to deploy an Azure Local in your environment. The article also contains the prerequisites and the preparation steps required to begin the deployment.
Important
ARM template deployment of Azure Local systems is targeted for deployments-at-scale. The intended audience for this deployment is IT administrators who have experience deploying Azure Local instances. We recommend that you deploy a system via the Azure portal first, and then perform subsequent deployments via the ARM template.
Prerequisites
- Completion of Register your machines with Azure Arc and assign deployment permissions. Make sure that:
- All machines are running the same version of OS.
- All the machines have the same network adapter configuration.
- For Azure Local 2411.3 and earlier versions, make sure to select the create-cluster-2411.3 template for deployment.
- For Azure Local 2503 and later versions, make sure to select the create-cluster template for deployment.
Step 1: Prepare Azure resources
Follow these steps to prepare the Azure resources you need for the deployment:
Create a service principal and client secret
To authenticate your system, you need to create a service principal and a corresponding Client secret for Arc Resource Bridge (ARB).
Create a service principal for ARB
Follow the steps in Create a Microsoft Entra application and service principal that can access resources via Azure portal to create the service principal and assign the roles. Alternatively, use the PowerShell procedure to Create an Azure service principal with Azure PowerShell.
The steps are also summarized here:
Sign in to the Microsoft Entra admin center as at least a Cloud Application Administrator. Browse to Identity > Applications > App registrations then select New registration.
Provide a Name for the application, select a Supported account type, and then select Register.
Once the service principal is created, go to the Enterprise applications page. Search for and select the SPN you created.
Under properties, copy the Application (client) ID and the Object ID for this service principal.
You use the Application (client) ID against the
arbDeploymentAppIDparameter and the Object ID against thearbDeploymentSPNObjectIDparameter in the ARM template.
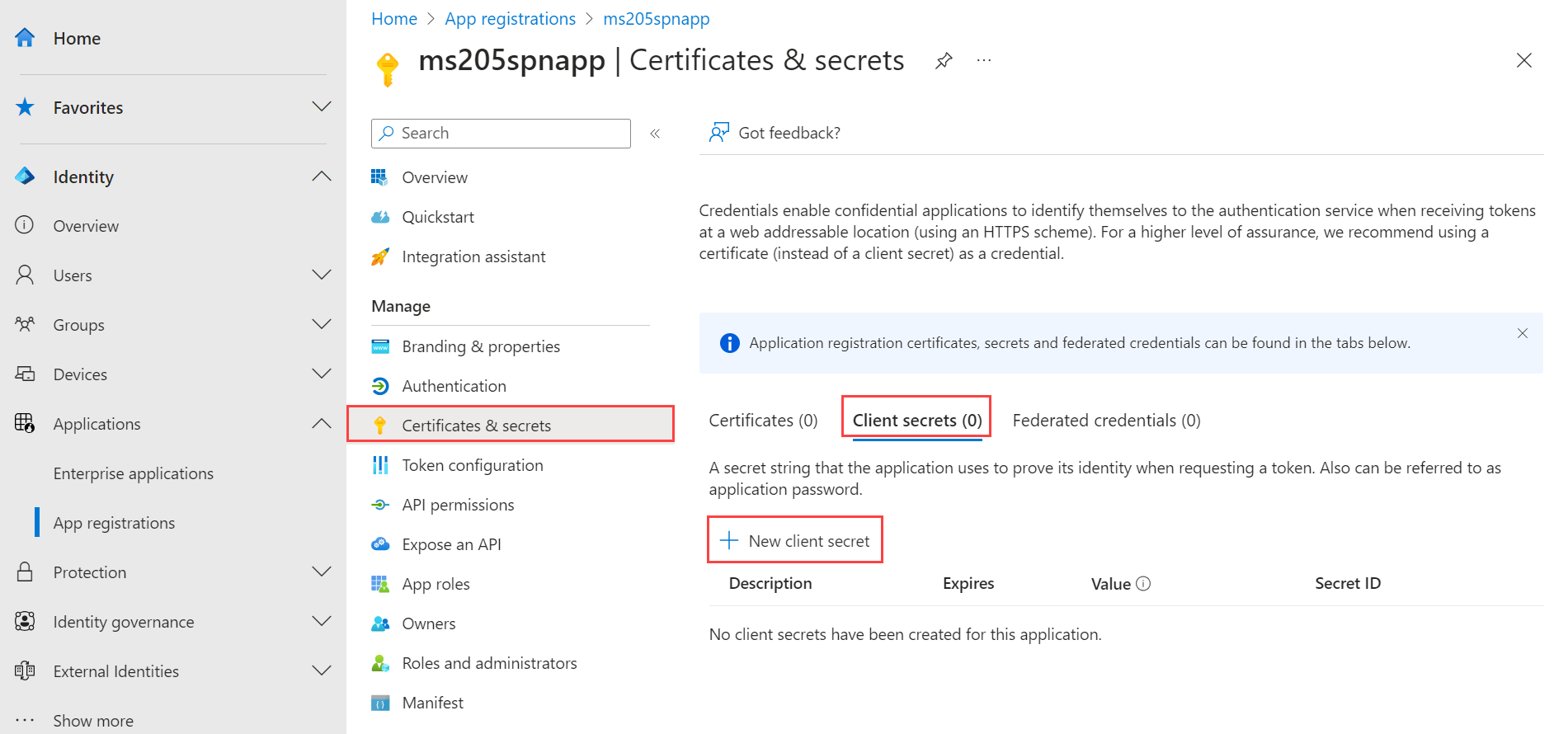
Create a client secret for ARB service principal
Go to the application registration that you created and browse to Certificates & secrets > Client secrets.
Select + New client secret.
Add a Description for the client secret and provide a timeframe when it Expires. Select Add.
Copy the client secret value as you use it later.
Note
For the application client ID, you will need it's secret value. Client secret values can't be viewed except for immediately after creation. Be sure to save this value when created before leaving the page.
You use the client secret value against the
arbDeploymentAppSecretparameter in the ARM.
Get the object ID for Azure Local Resource Provider
This object ID for the Azure Local Resource Provide (RP) is unique per Azure tenant.
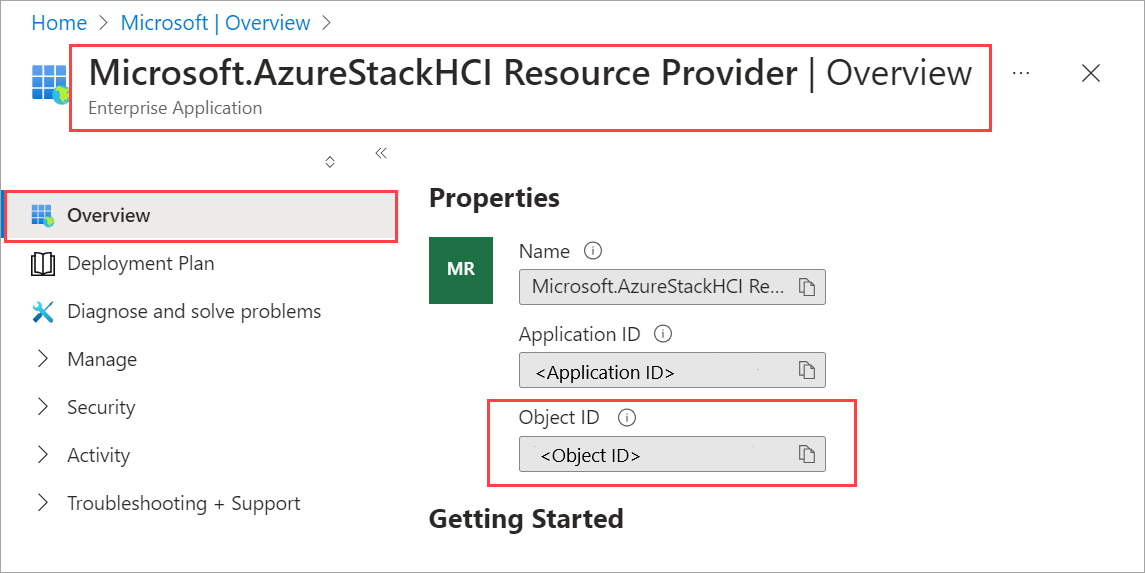
In the Azure portal, search for and go to Microsoft Entra ID.
Go to the Overview tab and search for Microsoft.AzureStackHCI Resource Provider.
Select the Service Principal Name that is listed and copy the Object ID.
Alternatively, you can use PowerShell to get the object ID of the Azure Local RP service principal. Run the following command in PowerShell:
Get-AzADServicePrincipal -DisplayName "Microsoft.AzureStackHCI Resource Provider"You use the Object ID against the
hciResourceProviderObjectIDparameter in the ARM template.
Step 2: Deploy using ARM template
An ARM template creates and assigns all the resource permissions required for deployment.
With all the prerequisite and preparation steps complete, you're ready to deploy using a known good and tested ARM deployment template and corresponding parameters JSON file. Use the parameters contained in the JSON file to fill out all values, including the values generated previously.
For an example of a parameter JSON file, see azuredeploy.parameters.json. For detailed descriptions of the parameters defined in this file, see ARM template parameters reference.
Important
Ensure that all parameters in the JSON file are filled out, including placeholders that appear as [“”], which indicate that the parameter expects an array structure. Replace these with actual values based on your deployment environment, or validation will fail.
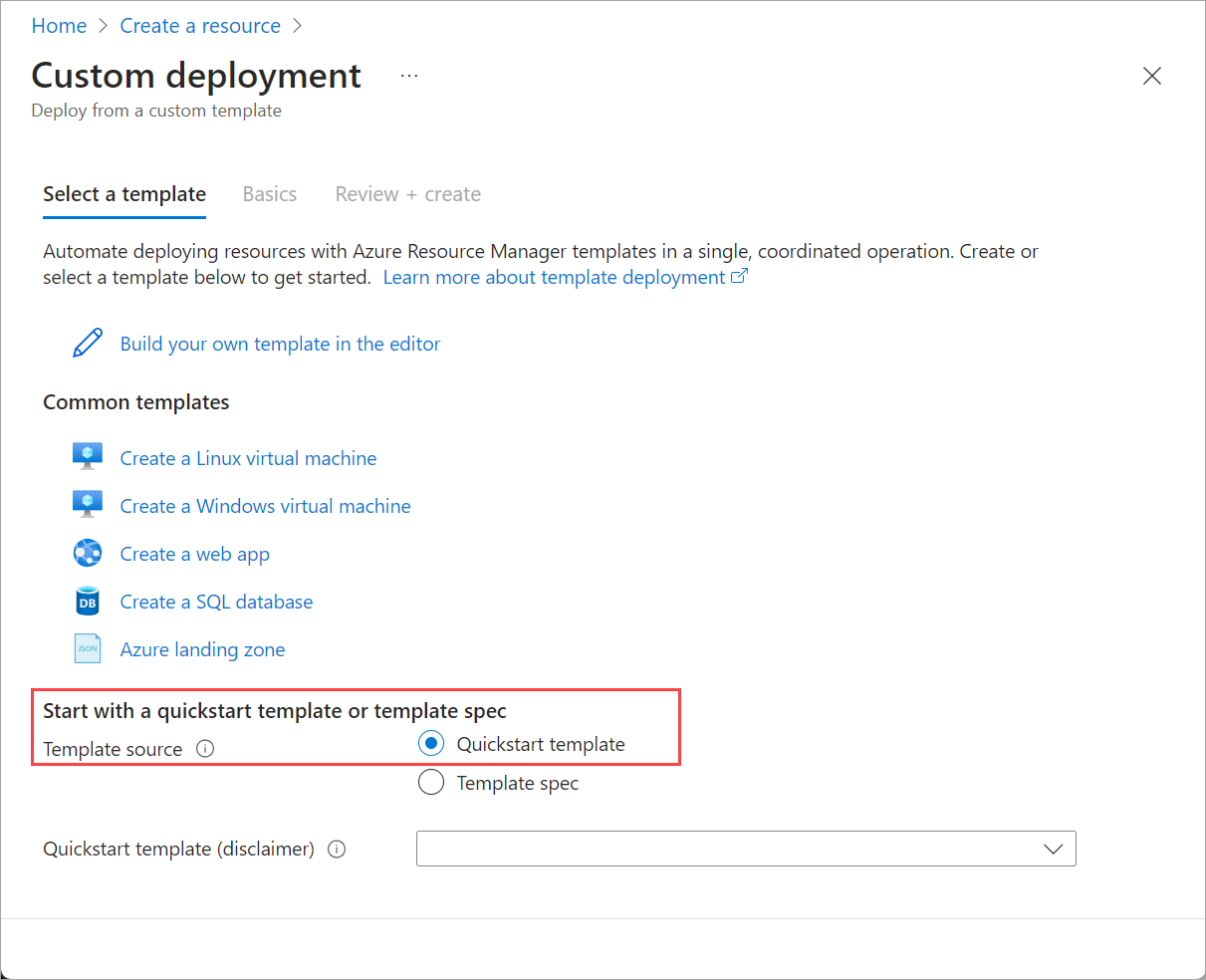
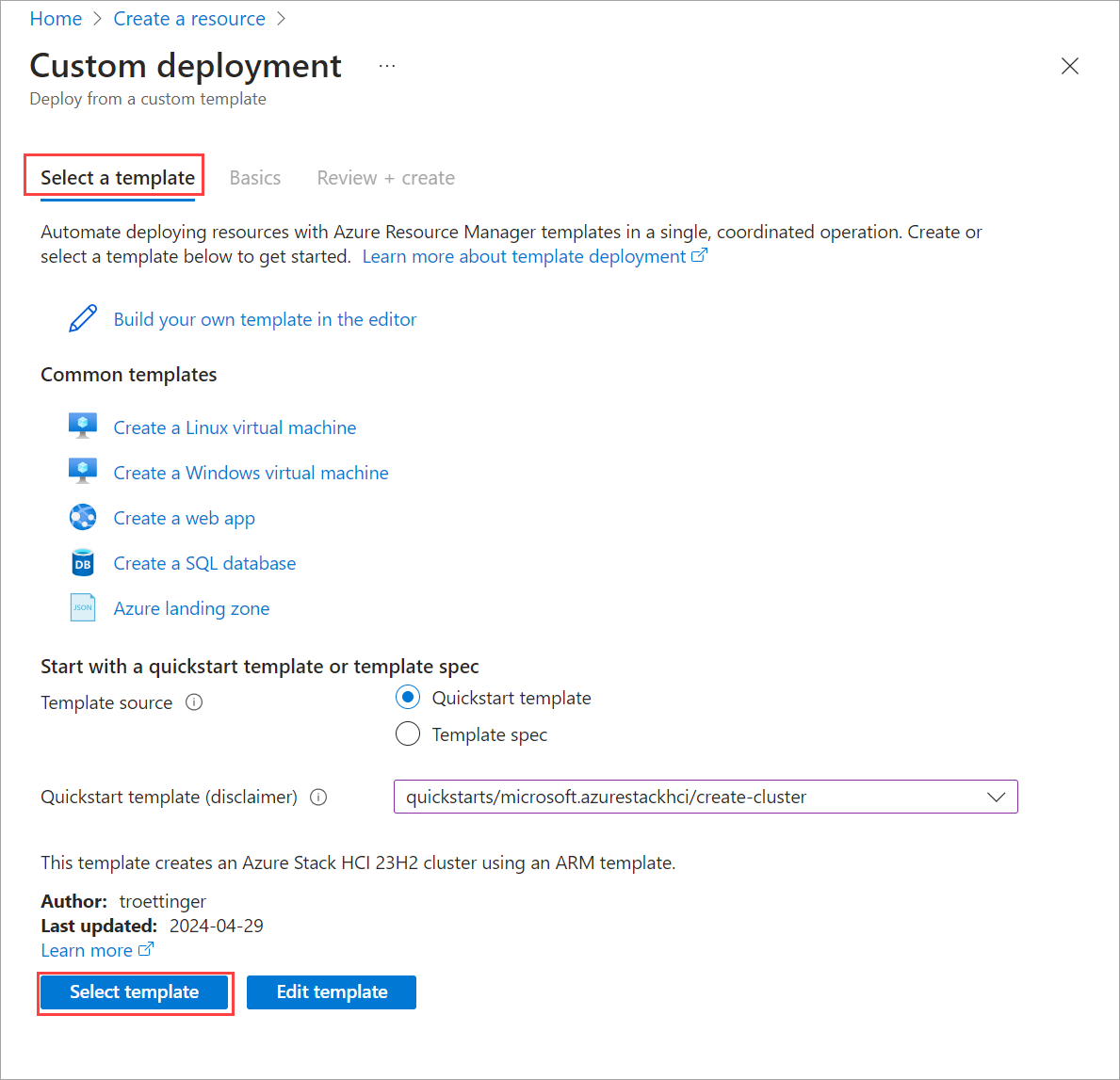
In the Azure portal, go to Home and select + Create a resource.
Select Create under Template deployment (deploy using custom templates).
Near the bottom of the page, find Start with a quickstart template or template spec section. Select Quickstart template option.
From the Quickstart template (disclaimer) dropdown list, select the create-cluster-2411.3 template.
When finished, select the Select template button.
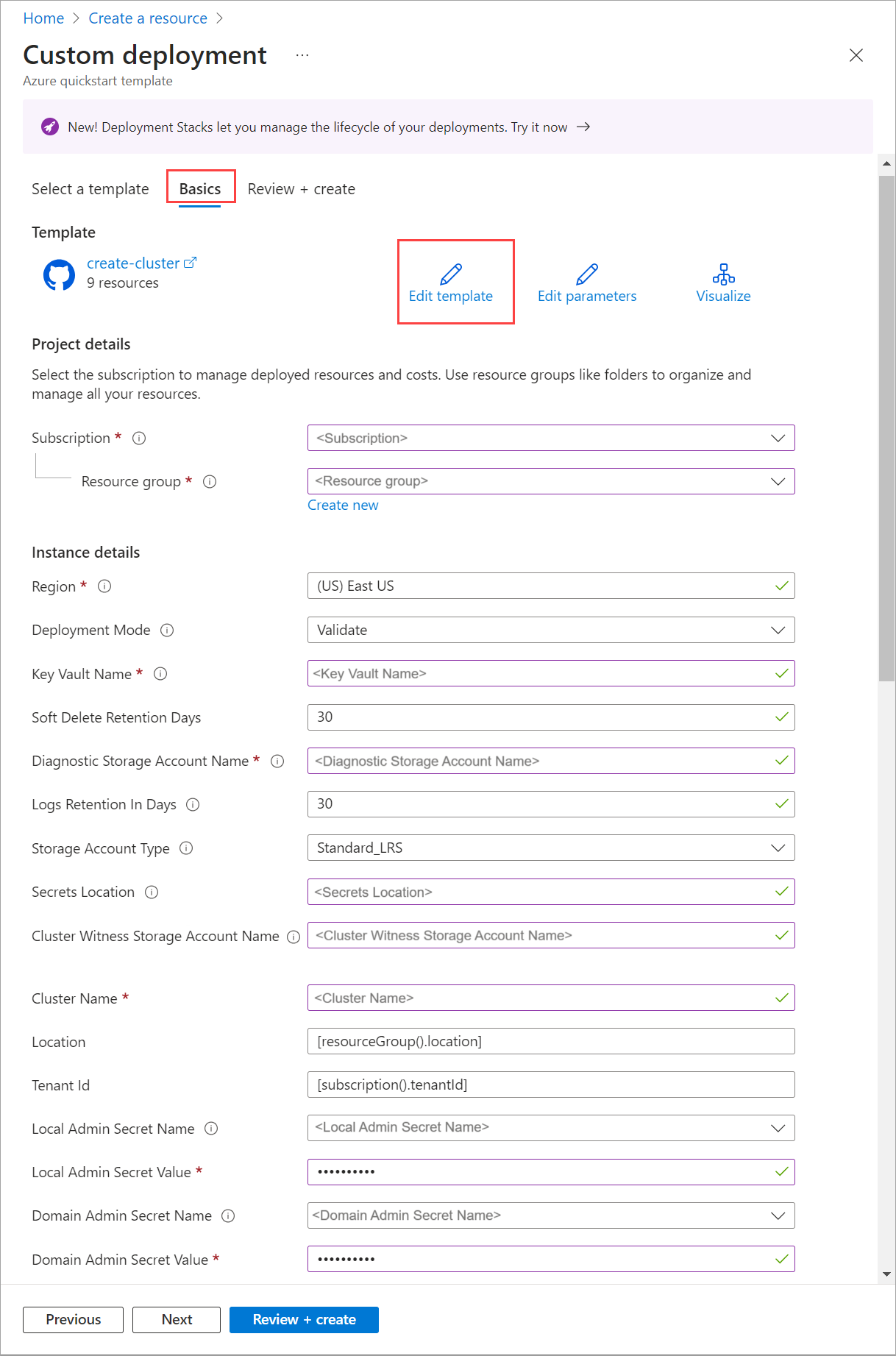
On the Basics tab, you see the Custom deployment page. You can select the various parameters through the dropdown list or select Edit parameters.
Note
For an example parameter file that shows the format of various inputs, such as
ArcNodeResourceId, see azuredeploy.parameters.json.
Use the Quickstart template (disclaimer) field to filter for the appropriate template. Type azurestackhci/create-cluster for the filter.
When finished, select the Select template button.
On the Basics tab, you see the Custom deployment page. You can select the various parameters through the dropdown list or select Edit parameters.
Note
For an example parameter file that shows the format of various inputs, such as
ArcNodeResourceId, see azuredeploy.parameters.json.
Edit parameters such as network intent or storage network intent. Once the parameters are all filled out, Save the parameters file.
Select the appropriate resource group for your environment.
Scroll to the bottom, and confirm that Deployment Mode = Validate.
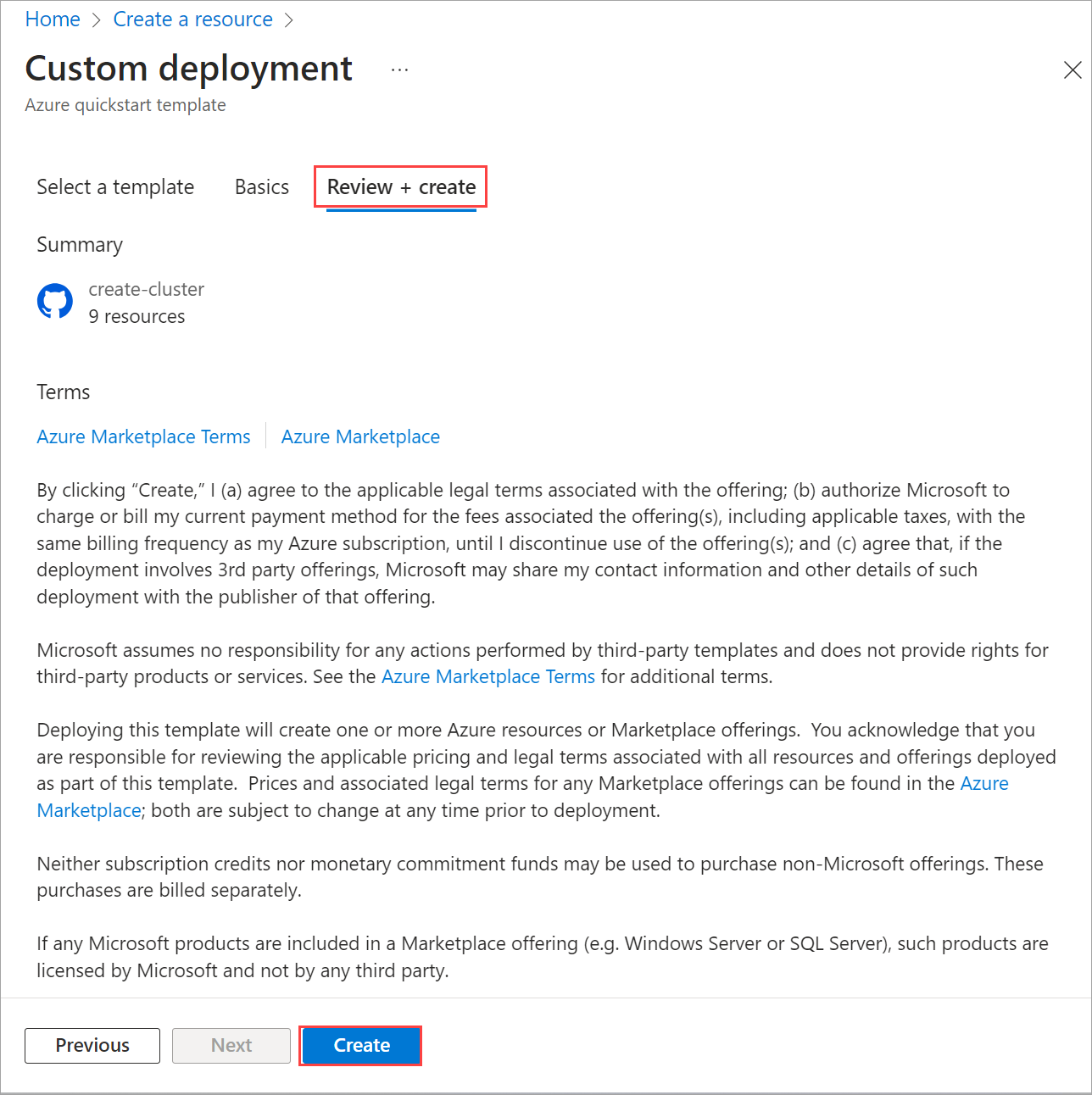
Select Review + create.
On the Review + Create tab, select Create. This creates the remaining prerequisite resources and validates the deployment. Validation takes about 10 minutes to complete.
Once validation is complete, select Redeploy.
On the Custom deployment screen, select Edit parameters. Load up the previously saved parameters and select Save.
At the bottom of the workspace, change the final value in the JSON from Validate to Deploy, where Deployment Mode = Deploy.
Verify that all the fields for the ARM deployment template are filled in by the Parameters JSON.
Select the appropriate resource group for your environment.
Scroll to the bottom, and confirm that Deployment Mode = Deploy.
Select Review + create.
Select Create. The deployment begins, using the existing prerequisite resources that were created during the Validate step.
The Deployment screen cycles on the cluster resource during deployment.
Once deployment initiates, there's a limited Environment Checker run, a full Environment Checker run, and cloud deployment starts. After a few minutes, you can monitor deployment in the portal.
In a new browser window, navigate to the resource group for your environment. Select the cluster resource.
Select Deployments.
Refresh and watch the deployment progress from the first machine (also known as the seed machine and is the first machine where you deployed the cluster). Deployment takes between 2.5 and 3 hours. Several steps take 40-50 minutes or more.
The step in deployment that takes the longest is Deploy Moc and ARB Stack. This step takes 40-45 minutes.
Once complete, the task at the top updates with status and end time.
You can also check out this community sourced template to Deploy an Azure Local instance using Bicep.
ARM template parameters reference
The following table describes the parameters that you define in the ARM template's parameters file:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| deploymentMode | Determines if the deployment process should only validate or proceed with full deployment: - Validate: Creates Azure resources for this system and validates your system's readiness to deploy. - Deploy: Performs the actual deployment after successful validation. |
| keyVaultName | Name of the Azure Key Vault to be used for storing secrets. For naming conventions, see Microsoft.KeyVault in the Naming rules and restrictions for Azure resources article. |
| softDeleteRetentionDays | Number of days that deleted items (such as secrets, keys, or certificates) are retained in an Azure Key Vault before they are permanently deleted. Specify a value between 7 and 90 days. You can’t change the retention period later. |
| diagnosticStorageAccountName | Name of the Azure Storage Account used to store key vault audit logs. This account is a locally redundant storage (LRS) account with a lock. For more information, see Azure Storage Account. For naming conventions, see Azure Storage account names. |
| logsRetentionInDays | Number of days that logs are retained. If you don't want to apply any retention policy and retain data forever, specify 0. |
| storageAccountType | Type of the Azure Storage Account to be used in the deployment. For example, Standard_LRS. |
| clusterName | Name of the Azure Local instance being deployed. This is the name that represents your cluster on cloud. It must be different from any of the node names. |
| ___location | Deployment ___location, typically derived from the resource group. For a list of supported Azure regions, see Azure requirements. |
| tenantId | Azure subscription tenant ID. For more information, see Find your Microsoft Entra tenant. |
| witnessType | Witness type for your Azure Local cluster. Witness type must be Cloud for a two-node cluster. It can be empty for other cluster sizes. For more information on cloud witness, see Deploy a quorum witness. |
| clusterWitnessStorageAccountName | Name of the storage account used for cluster witness. For more information, see Azure Storage Account. For naming conventions, see Azure Storage account names. |
| localAdminUserName | Username for the local administrator for all the machines in your system. The credentials are identical for all the machines in your system. For more information, see Review deployment prerequisites for Azure Local. |
| localAdminPassword | Password for the local administrator for all the machines in your system. The credentials are identical for all the machines in your system. For more information, see Review deployment prerequisites for Azure Local. |
| AzureStackLCMAdminUsername | Username for the LCM admin. For more information, see Review deployment prerequisites for Azure Local. |
| AzureStackLCMAdminPasssword | Password for the LCM admin. For more information, see Review deployment prerequisites for Azure Local. |
| hciResourceProviderObjectID | Object ID of the Azure Local Resource Provider. For more information, see Get the object ID for Azure Local Resource Provider. |
| arcNodeResourceIds | Array of resource IDs of the Azure Arc-enabled servers that are part of this Azure Local cluster. |
| domainFqdn | Fully-qualified ___domain name (FQDN) for the Active Directory Domain Services prepared for deployment. |
| namingPrefix | Prefix used for all objects created for the Azure Local deployment. |
| adouPath | Path of the Organizational Unit (OU) created for this deployment. The OU can't be at the top level of the ___domain. For example: OU=Local001,DC=contoso,DC=com. |
| securityLevel | Security configuration profile to be applied to the Azure Local cluster during deployment. The default is Recommended. |
| driftControlEnforced | Drift control setting to reapply the security defaults regularly. For more information, see Security features for Azure Local. |
| credentialGuardEnforced | Credential Guard setting that uses virtualization-based security to isolate secrets from credential-theft attacks. For more information, see Manage security defaults for Azure Local. |
| smbSigningEnforced | Setting for signing SMB traffic between this Azure Local cluster and others to help prevent relay attacks. For more information, see Overview of Server Message Block signing. |
| smbClusterEncryption | SMB cluster traffic setting for encrypting traffic between servers in the cluster on your storage network. For more information, see SMB encryption. |
| bitlockerBootVolume | BitLocker encryption setting for encrypting OS volume on each server. For more information, see Manage BitLocker encryption on Azure Local. |
| bitlockerDataVolumes | BitLocker encryption setting for encrypting cluster shared volumes (CSVs) created on this system during deployment. For more information, see Manage BitLocker encryption on Azure Local. |
| wdacEnforced | Application Control setting to control which drivers and apps are allowed to run directly on each server. For more information, see Manage Application Control for Azure Local. |
| streamingDataClient | Specifies whether telemetry data streaming from the Azure Local cluster to Microsoft is enabled. |
| euLocation | Specifies whether to send and store telemetry and diagnostic data within the European Union (EU). |
| episodicDataUpload | Episodic diagnostic data setting to specify whether to collect log data and upload to Microsoft to assist with troubleshooting and support. For more information, see Crash dump collection. |
| configurationMode | Storage volume configuration mode. The supported values are: - Express: Creates one thinly provisioned volume and storage path per machine for workloads to use. This is in addition to the required one infrastructure volume per cluster. - InfraOnly: Creates only the required one infrastructure volume per cluster. You need to create workload volumes and storage paths later. - KeepStorage: Preserves existing data drives that contain a Storage Spaces pool and volumes. |
| subnetMask | The subnet mask for the management network used by the Azure Local deployment. |
| defaultGateway | The default gateway for deploying an Azure Local cluster. |
| startingIPAddress | The first IP address in a contiguous block of at least six static IP addresses on your management network's subnet, omitting addresses already used by the machines. These IPs are used by Azure Local and internal infrastructure (Arc Resource Bridge) that's required for Arc VM management and AKS Hybrid. |
| endingIPAddress | The last IP address in a contiguous block of at least six static IP addresses on your management network's subnet, omitting addresses already used by the machines. These IPs are used by Azure Local and internal infrastructure (Arc Resource Bridge) that's required for Arc VM management and AKS Hybrid. |
| dnsServers | List of DNS server IPs. |
| useDhcp | Indicates whether to use Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) for hosts and cluster IPs. If not declared, the deployment will default to static IPs. If TRUE, gateway and DNS servers are not required. |
| physicalNodesSettings | Array of physical nodes with their IP addresses. |
| networkingType | Type of networking. For example, switchedMultiServerDeployment. For more information, see Specify network settings. |
| networkingPattern | Pattern used for networking. For example, hyperConverged. |
| intentList | List of deployment intents. |
| storageNetworkList | List of storage networks. |
| storageConnectivitySwitchless | Specifies whether storage connectivity is configured without network switches. |
| enableStorageAutoIp | Specifies whether automatic IP assignment is enabled. |
| customLocation | Custom ___location for deployment. |
| sbeVersion | Version of the Solution Builder Extension (SBE) to be used during an Azure Local deployment. |
| sbeFamily | Family or category of the SBE package being applied during deployment. |
| sbePublisher | Publisher or vendor of the SBE. |
| sbeManifestSource | Source ___location of the SBE manifest file. |
| sbeManifestCreationDate | Creation date of the SBE manifest. |
| partnerProperties | List of partner-specific properties. |
| partnerCredentiallist | List of partner credentials. |
Troubleshoot deployment issues
If the deployment fails, you should see an error message on the deployments page.
On the Deployment details, select the error details.
Copy the error message from the Errors blade. You can provide this error message to Microsoft support for further assistance.
Known issues for ARM template deployment
This section contains known issues and workarounds for ARM template deployment.
Role assignment already exists
Issue: In this release, you may see Role assignment already exists error. This error occurs if the Azure Local instance deployment was attempted from the portal first and the same resource group was used for ARM template deployment. You see this error on the Overview > Deployment details page for the applicable resource. This error indicates that an equivalent role assignment was already done by another identity for the same resource group scope and the ARM template deployment is unable to perform role assignment.
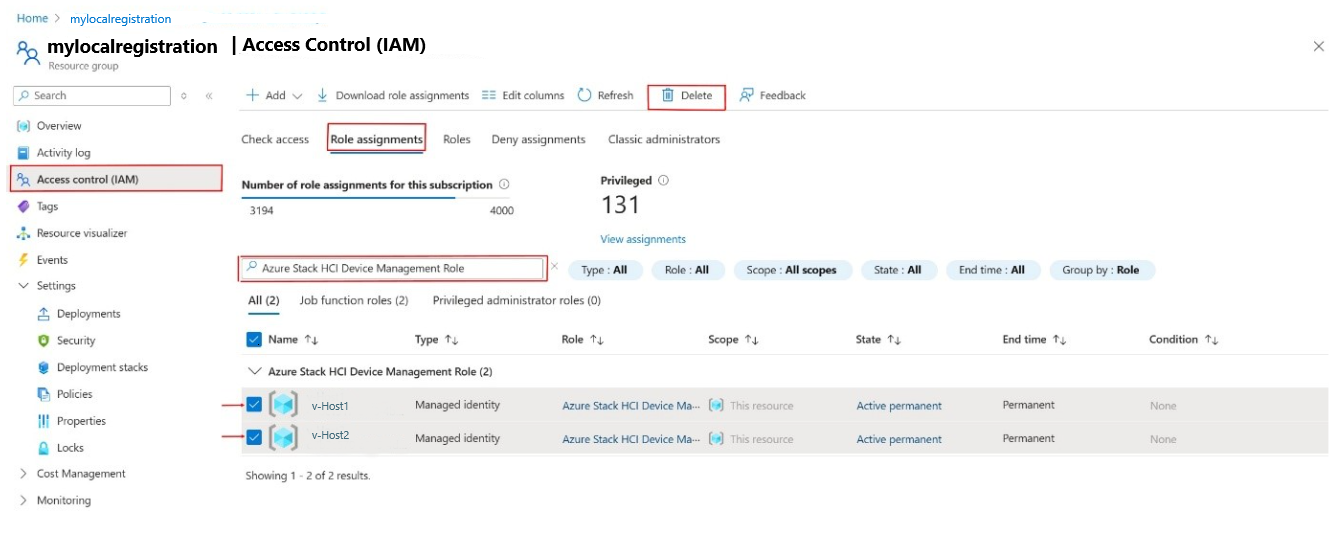
Workaround: The failed resource on the Deployment details page specifies the role assignment name. If the resource name is AzureStackHCIDeviceManagementRole-RoleAssignment then role assignment failed for the Azure Stack HCI Device Management Role. Note this role name and go to Resource Group > Access Control (IAM) > Role Assignments. Search for the corresponding name and delete the existing role assignments there. Redeploy your template.
Tenant ID, application ID, principal ID, and scope aren't allowed to be updated
Issue: Role assignment fails with error Tenant ID, application ID, principal ID, and scope aren't allowed to be updated. You see this error on the Overview > Deployment details page for the applicable resource. This error could show up when there are zombie role assignments in the same resource group. For example, when a prior deployment was performed and the resources corresponding to that deployment were deleted but the role assignment resources were left around.
Workaround: To identify the zombie role assignments, go to Access control (IAM) > Role assignments > Type : Unknown tab. These assignments are listed as Identity not found. Unable to find identity. Delete such role assignments and then retry ARM template deployment.
License sync issue
Issue: In this release, you may encounter license sync issue when using ARM template deployment.
Workaround: After the system completes the validation stage, we recommend that you don't initiate another ARM template deployment in Validate mode if your system is in Deployment failed state. Starting another deployment resets the system properties, which could result in license sync issues.