Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
In Microsoft Defender for Cloud, resources and workloads are assessed against built-in and custom security standards, which are applied in your Azure subscriptions, Amazon Web Services (AWS) accounts, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) projects. Based on those assessments, security recommendations provide practical steps to remediate security issues and improve security posture.
Defender for Cloud proactively uses a dynamic engine that assesses the risks in your environment, while it considers the potential for exploitation and the potential business effect on your organization. The engine prioritizes security recommendations based on the risk factors of each resource. The context of the environment determines these risk factors. This context includes the resource's configuration, network connections, and security posture.
Prerequisites
You must enable Defender Cloud Security Posture Management (Defender CSPM) on your environment.
Note
By default, recommendations are included with Defender for Cloud, but you can't see risk prioritization unless you enable Defender CSPM on your environment.
Review the recommendations page
Review recommendations and make sure all the details are correct before you resolve them.
Sign in to the Azure portal.
Go to Defender for Cloud > Recommendations.
Select a recommendation.
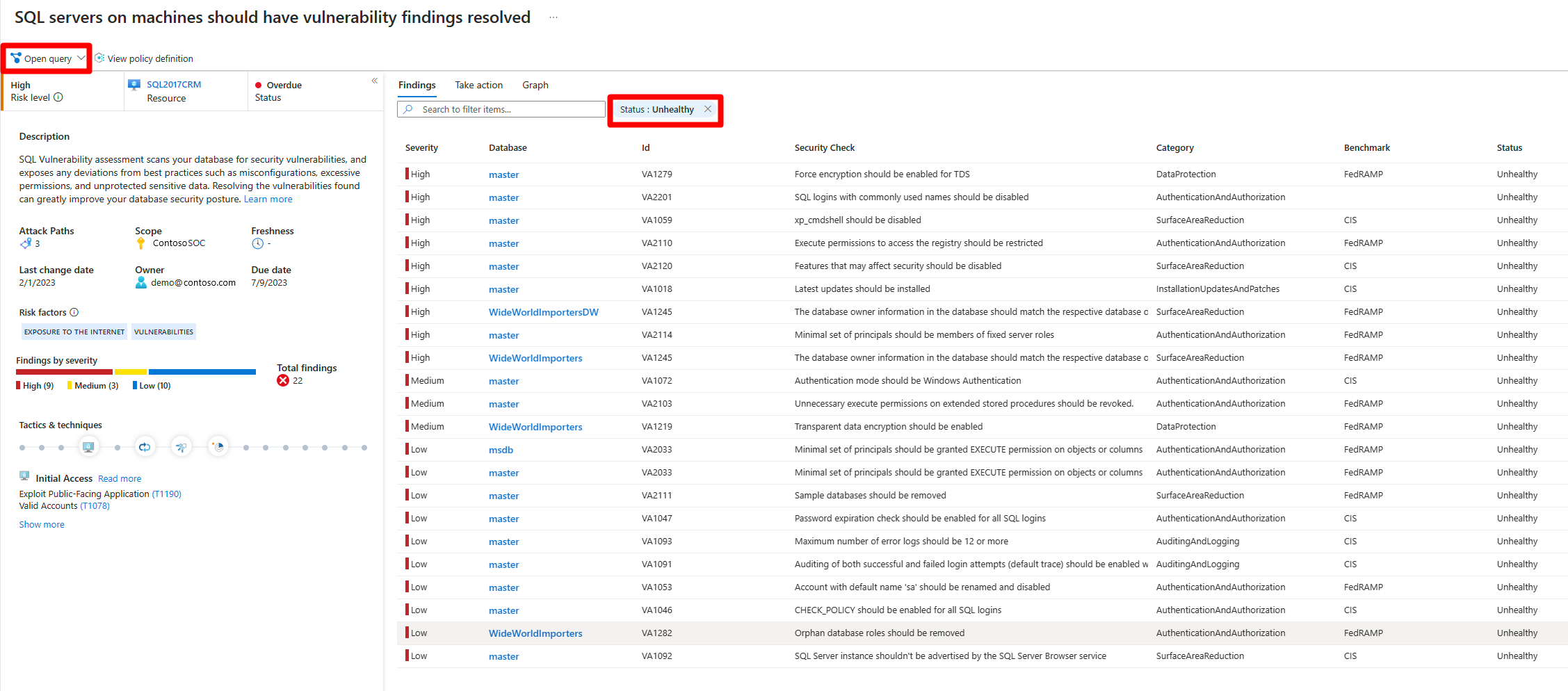
On the recommendation page, review the following details:
- Risk level: The vulnerability and business effect of the underlying security issue, considering the environmental resource context like internet exposure, sensitive data, lateral movement, and more.
- Risk factors: Environmental factors of the resource affected by the recommendation, which influence the vulnerability and business effect of the underlying security issue. Examples of risk factors include internet exposure, sensitive data, and lateral movement potential.
- Resource: The name of the affected resource.
- Status: The status of the recommendation, like unassigned, on time, or overdue.
- Description: A brief description of the security issue.
- Attack Paths: The number of attack paths.
- Scope: The affected subscription or resource.
- Freshness: The freshness interval of the recommendation.
- Last change date: The date when this recommendation was last changed.
- Severity: The severity of the recommendation: High, Medium, or Low. More details are provided later in this article.
- Owner: The person assigned to the recommendation.
- Due date: The assigned due date for resolving the recommendation.
- Tactics & techniques: The tactics and techniques mapped to MITRE ATT&CK.
Explore a recommendation
You can interact with recommendations in multiple ways. If an option isn't available, that means it's not relevant to the recommendation.
Sign in to the Azure portal.
Go to Defender for Cloud > Recommendations.
Select a recommendation.
In the recommendation, you can perform these actions:
- To view detailed information about the affected resources with an Azure Resource Graph Explorer query, select Open query.
- To view the Azure Policy entry for the underlying recommendation (if relevant), select View policy definition.
- To view all resources the recommendation applies to, select View recommendation for all resources.
In Take action:
- Remediate: A description of the manual steps required to resolve the security issue on the affected resources. For recommendations with the Fix option, you can select View remediation logic before applying the suggested fix to your resources.
- Recommendation owner and set due date: If you enable a governance rule for the recommendation, you can assign an owner and due date.
- Exempt: You can exempt resources from the recommendation or disable specific findings by using disable rules.
- Workflow automation: Set a logic app to trigger with the recommendation.
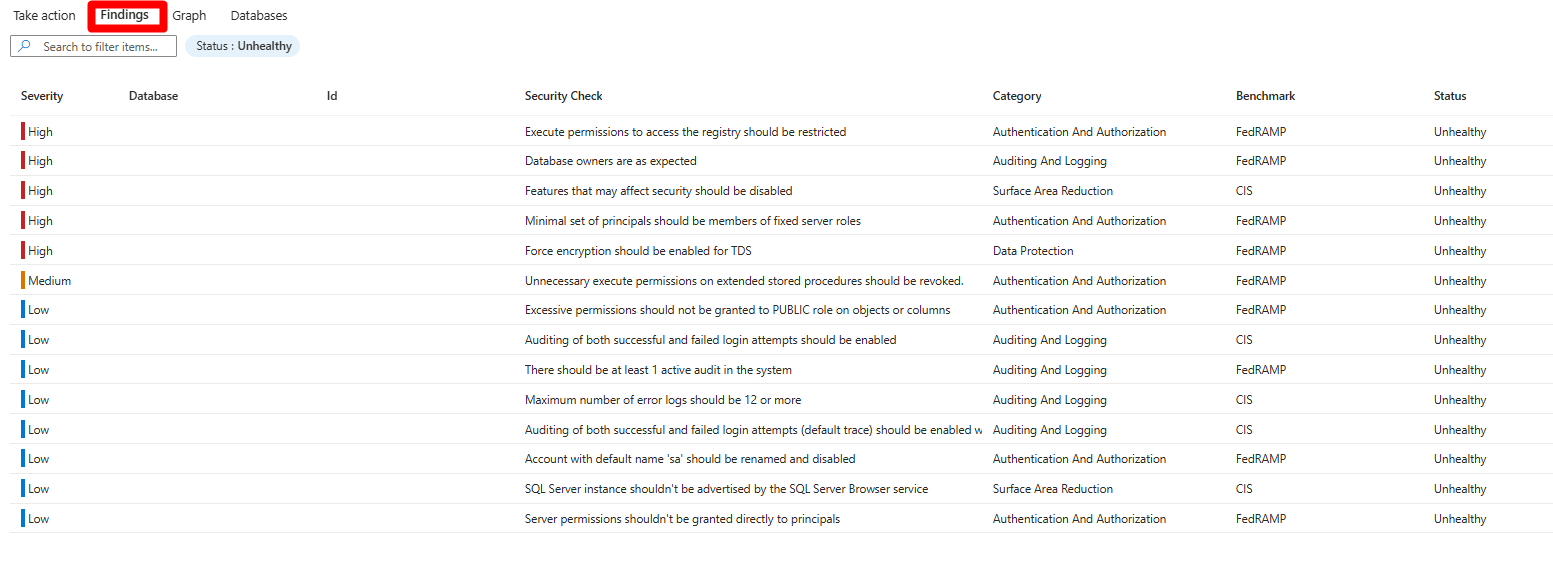
In Findings, you can review affiliated findings by severity.
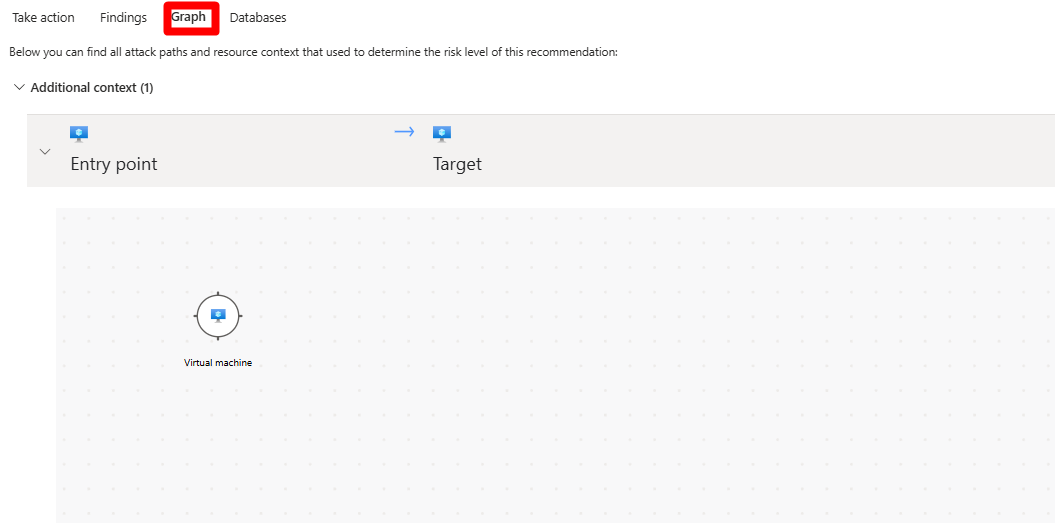
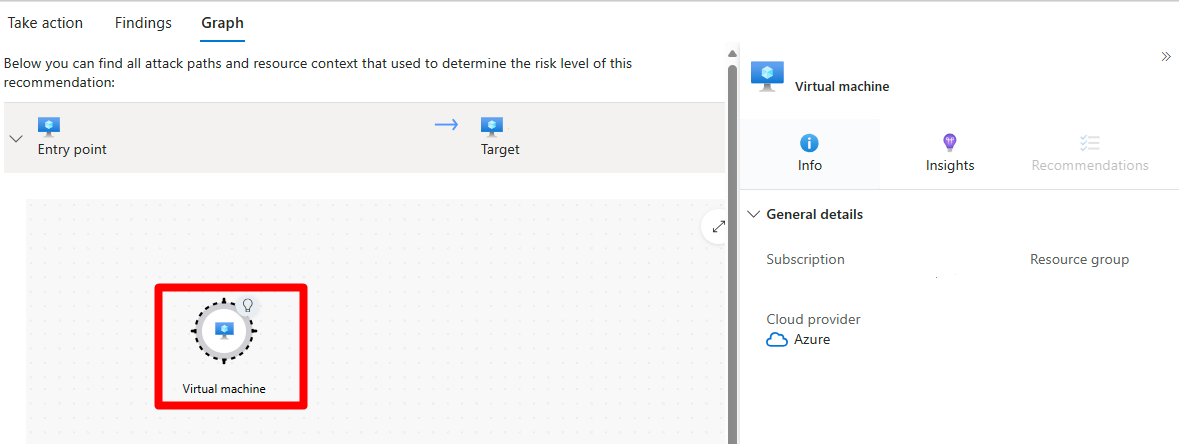
In Graph, you can view and investigate all the context that's used for risk prioritization, including attack paths. You can select a node in an attack path to view the details of the selected node.
To view more details, select a node.
Select Insights.
To view details, select a vulnerability from the dropdown menu.
(Optional) To view the associated recommendation page, select Open the vulnerability page.
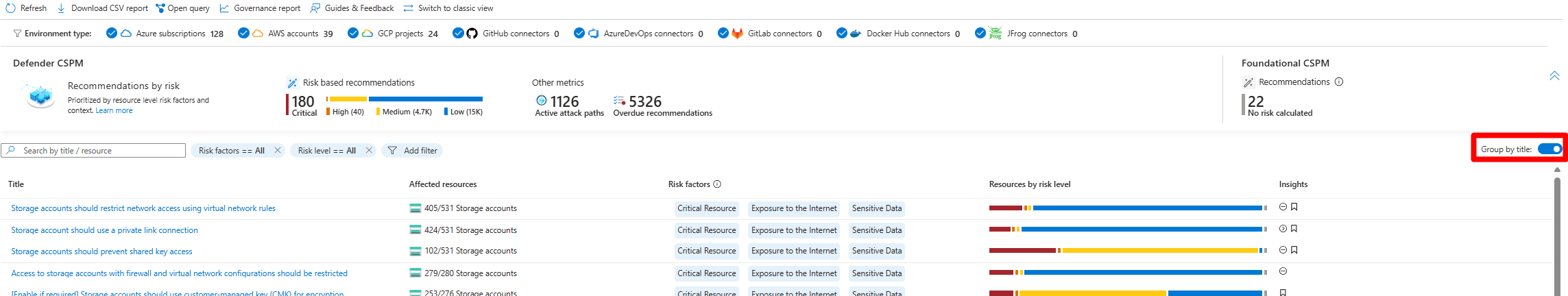
Group recommendations by title
You can group recommendations by title with the Defender for Cloud recommendation page. This feature is useful when you want to remediate a recommendation that affects multiple resources due to a specific security issue.
Sign in to the Azure portal.
Go to Defender for Cloud > Recommendations.
Select Group by title.
Manage your assigned recommendations
Defender for Cloud supports governance rules for recommendations. You can assign a recommendation owner or a due date. You can help ensure accountability by using governance rules, which also support a service-level agreement (SLA) for recommendations.
- Recommendations appear as On time until their due date passes. Then they change to Overdue.
- When a recommendation isn't classified as Overdue, it doesn't affect your Microsoft Secure Score.
- You can also apply a grace period so that overdue recommendations don't affect your Secure Score.
Learn more about how to configure governance rules.
To see all of your assigned recommendations:
Sign in to the Azure portal.
Go to Defender for Cloud > Recommendations.
Select Add filter > Owner.
Select your user entry.
Select Apply.
In the recommendation results, review the recommendations, including affected resources, risk factors, attack paths, due dates, and status.
Select a recommendation to review it further.
To make changes to an assignment, complete the following steps:
Go to Take action > Change owner & due date.
Select Edit assignment to change the recommendation owner or due date.
If you select a new remediation date, specify why remediation should be completed by that date in Justification.
Select Save.
Note
When you change the expected completion date, the due date for the recommendation doesn't change, but security partners can see that you plan to update the resources by the specified date.
By default, the owner of the resource receives a weekly email that shows all the recommendations assigned to them.
You can also use the Set email notifications option to:
- Override the default weekly email to the owner.
- Notify owners weekly with a list of open or overdue tasks.
- Notify the owner's direct manager with an open task list.
Review recommendations in Azure Resource Graph
You can use Azure Resource Graph to write a Kusto Query Language (KQL) query to query Defender for Cloud security posture data across multiple subscriptions. Azure Resource Graph provides an efficient way to query at scale across cloud environments by viewing, filtering, grouping, and sorting data.
Sign in to the Azure portal.
Go to Defender for Cloud > Recommendations.
Select a recommendation.
Select Open query.
You can open the query in one of two ways:
- Query returning affected resource: Returns a list of all of the resources that the recommendation affects.
- Query returning security findings: Returns a list of all security issues that the recommendation found.
Select run query.
Review the results.
How are recommendations classified?
Every security recommendation from Defender for Cloud is given one of three severity ratings.
High severity
We recommend that you address these recommendations immediately. They indicate that there's a critical security vulnerability that an attacker could exploit to gain unauthorized access to your systems or data.
Examples of high severity recommendations include:
- Unprotected secrets on a machine.
- Overly permissive inbound network security group rules.
- Clusters that allow images to be deployed from untrusted registries.
- Unrestricted public access to storage accounts or databases.
Medium severity
These recommendations indicate a potential security risk. We recommend that you address these recommendations in a timely manner, but they might not require immediate attention.
Examples of medium severity recommendations include:
- Containers that share sensitive host namespaces.
- Web apps that don't use managed identities.
- Linux machines that don't require SSH keys during authentication.
- Unused credentials left in the system after 90 days of inactivity.
Low severity
These recommendations indicate a relatively minor security issue that can be addressed at your convenience.
Examples of low severity recommendations include:
- The use of local authentication instead of Microsoft Entra ID.
- Health issues with your endpoint protection solution.
- Users not following best practices with network security groups.
- Misconfigured logging settings, which might make it harder to detect and respond to security incidents.
An organization's internal policies might differ from Microsoft's classification of a specific recommendation. We recommend that you always carefully review each recommendation and consider its potential effect on your security posture before you decide how to address it.
Note
Defender CSPM customers have access to a richer classification system where recommendations feature a Risk level determination that utilizes the context of the resource and all related resources. Learn more about risk prioritization.
Example
In this example, the Recommendation details page shows 15 affected resources:
When you open and run the underlying query, Azure Resource Graph Explorer returns the same affected resources for this recommendation.