Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
The Azure MCP Server uses the Model Context Protocol (MCP) to standardize integrations between AI apps and external tools and data sources, allowing for AI systems to perform operations that are context-aware of your Azure resources.
In this article, you learn how to complete the following tasks:
- Install and authenticate to the Azure MCP Server.
- Connect to Azure MCP Server using GitHub Copilot agent mode in Visual Studio.
- Run prompts to test Azure MCP Server operations and interact with Azure resources.
Prerequisites
- An Azure account with an active subscription
- Visual Studio
- .NET 10 OR Node.js LTS installed
Install the Azure MCP Server
Visual Studio uses a file named mcp.json to check for MCP Server configurations, including configurations set up by other development environments. MCP server configurations are read from the following directories, in the following order:
%USERPROFILE%\.mcp.json: Serves as a global MCP server configuration for a specific user. Add an MCP server here to make it load for all Visual Studio solutions.<SOLUTIONDIR>\.vs\mcp.json: Specific to Visual Studio and only loads the specified MCP servers for a specific user, for the specified solution.<SOLUTIONDIR>\.mcp.json: A solution-level MCP configuration that you can track in source control for a repo.<SOLUTIONDIR>\.vscode\mcp.json: Scoped to the repository/solution and typically not included in source control.<SOLUTIONDIR>\.cursor\mcp.json: Scoped to the repository/solution and typically not included in source control.
Note
Some of these locations require .mcp.json while others require mcp.json.
Azure MCP Server is available as a NuGet package or as an NPM package. The following options demonstrate two of the most common approaches to connect to Azure MCP Server from Visual Studio.
Complete the following steps to install Azure MCP Server for a specific directory:
Create a new file at the root of your solution named
.mcp.json. Use Visual Studio to edit this file so that its JSON schema is automatically applied.Inside the
.mcp.jsonfile, add the following JSON for your preferred package:NuGet:
{ "servers": { "Azure MCP Server": { "command": "dnx", "args": [ "Azure.Mcp", "--source", "https://api.nuget.org/v3/index.json", "--yes", "--", "azmcp", "server", "start" ], "type": "stdio" } } }NPM:
{ "servers": { "Azure MCP Server": { "command": "npx", "args": [ "-y", "@azure/mcp@latest", "server", "start" ] } } }Save your changes.
Open GitHub Copilot and select Agent Mode.
Select the tools icon to view the available tools. Search for Azure MCP Server to filter the results.

Authenticate to Azure
Azure MCP Server provides a seamless authentication experience using Azure accounts and Microsoft Entra ID. To use Azure MCP Server, you must first authenticate to Azure using local development tools such as the Azure CLI, Azure Developer CLI, Visual Studio, or Visual Studio Code. Azure MCP Server automatically discovers your credentials from these tools and uses them to authenticate to Azure services.
For example, to sign in using the Azure CLI:
az loginVerify your authentication status by running the following command to see which account and subscription you're currently signed in with:
az account showEnsure your user account has the appropriate role assignments for the Azure services you want to interact with. The Azure resources you intend to access with Azure MCP Server must already exist within your Azure subscription. For example, common role assignments include:
- Blob Storage Data Contributor - Read and write blob data in storage accounts.
- Storage Account Contributor - Manage storage account configurations.
- Contributor - General resource management across your subscription.
- Reader - Read-only access to Azure resources.
For more information about role assignments and local development authentication, see Authenticate .NET apps to Azure services during local development.
Use prompts to test the Azure MCP Server
Open GitHub Copilot and select Agent Mode.
Enter a prompt that causes the agent to use Azure MCP Server tools, such as List my Azure resource groups.
In order to authenticate Azure MCP Server, Copilot prompts you to sign-in to Azure using the browser.
Note
Copilot doesn't prompt you to sign-in to Azure if you're already authenticated via other local tooling such as the Azure CLI.
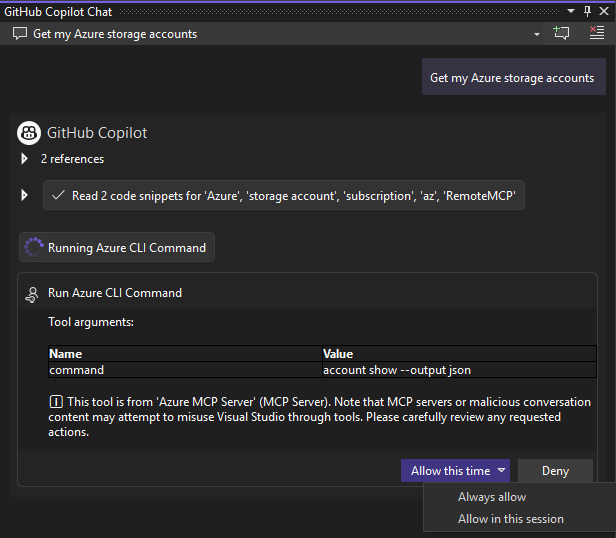
Copilot requests permission to run the necessary Azure MCP Server operation for your prompt. Select Allow this time or use the arrow to select a more specific behavior:
- Always allow sets the operation to always run for any GitHub Copilot Agent Mode session or any Visual Studio Code workspace.
- Allow in this session always runs the operation in the current GitHub Copilot Agent Mode session.
The output for the previous prompt should resemble the following text:
The following resource groups are available for your subscription: 1. **DefaultResourceGroup-EUS** (Location: `eastus`) 2. **rg-testing** (Location: `centralus`) 3. **rg-azd** (Location: `eastus2`) 4. **msdocs-sample** (Location: `southcentralus`) 5. **ai-testing** (Location: `eastus2`) Let me know if you need further details or actions related to any of these resource groups!Explore and test the Azure MCP operations using other relevant prompts, such as:
List all of the storage accounts in my subscription Get the available tables in my storage accounts