Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Azure DevOps Services | Azure DevOps Server | Azure DevOps Server 2022 | Azure DevOps Server 2020
Scrum methods use iteration paths, or sprints, to plan work for teams within specific time periods and cadences. Useful tools for implementing Scrum practices in Azure Boards include filtered backlogs and boards based on iteration paths. You can use Scrum to schedule and plan sprints, update your board, and monitor sprint burndown.
For an introduction to Scrum, see What is Scrum?
Scrum in Azure Boards
The general sequence of steps for implementing Scrum in Azure Boards is as follows. For more information, select each linked article.
Configure teams and sprints
- Define project-level iteration paths and set dates.
- Add project-level area paths, or add an area path when you configure each team.
- Add teams.
- Select team-level iteration paths.
Create the team backlog
Note
If you don't see the desired work items on your backlog or board, see Create and manage your backlog. For more information, see What is Azure Boards?
Assign backlog items to sprints
You can quickly assign work items to a sprint by dragging and dropping them from the product backlog to the sprint. To get started with Scrum, you can use the default sprints that are predefined for each Azure DevOps project.
- Assign backlog items to a sprint.
- Add tasks to backlog items.
- Set sprint capacity.
- Adjust work to fit sprint capacity.
- Share your sprint plan.
Monitor sprint progress
Close out a sprint
Sprint backlogs
Sprint backlogs and boards provide filtered views of work items for teams assigned to specific iteration paths or sprints. Sprints are defined for a project and then selected for teams.
From the team backlog, you can map work to an iteration path using drag-and-drop, and then view the work for each sprint in a separate backlog. The sprint backlog contains a filtered subset of backlog items whose iteration path corresponds to the chosen sprint.
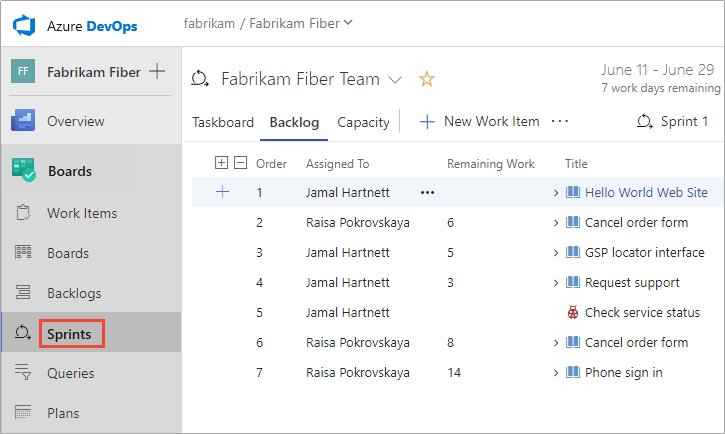
If you work with several teams and each team wants their own backlog view, you can create more teams. Each team then gets access to their own set of Agile tools that filter work items to the team's default area path and iteration path.
Planning view
Each sprint you select for your team provides access to a sprint backlog, board, and other Agile tools for planning and tracking work. The Planning view provides an overview of your sprint planning.
From the project backlog or any sprint backlog page, select the View options icon and then select Planning. The sprints selected for your team appear in a side pane.
To select a sprint backlog, you can choose one of the sprint links from the Planning pane, or you can choose it from the sprint selector on a sprint backlog page.
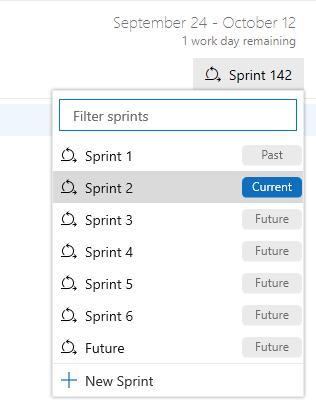
If no sprints are listed in the Planning pane or sprint dropdown list, you can add sprints or select existing sprints for your team. For more information, see Define sprints.
Note
The Planning pane shows only the current sprint and the next 10 future sprints, even if the team has more sprints selected.
Capacity tracking
Once you define iteration paths and configure team iterations, you can start using Agile capacity planning tools to plan the work your team can commit to during a sprint. The capacity planning and capacity bar tools support this task.
Capacity planning
Use the team capacity tool under the Capacity tab to set individual team member capacity and days off, and holidays or shared days off for the entire team. When you set team capacity, the team knows the exact total number of work hours or days they have for each sprint. For more information, see Set capacity for the team and team members.
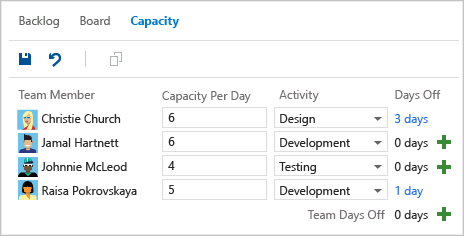
Capacity bars
The Work details pane shows capacity bars for the overall team, by Activity, or by Assigned to for each team member working during a sprint. You can use capacity bars to quickly see who is over, at, or under capacity for the sprint.
To see capacity bars, select the View options icon and then select Work details. As you add individual team members and assignments in the planning tool, a capacity bar appears and updates for that individual. Team and individual capacity always reflect capacity from the current day until the end of the sprint.
Capacity bars update with each of these activities:
- Work is assigned with nonzero remaining work.
- Remaining work changes.
- Dates change within the sprint cycle.

Task board and burndown chart
During a sprint, you can use the task board and sprint burndown chart to track progress. The sprint burndown chart provides an at-a-glance visual to determine if your team is on track to meet its sprint plan.
Task board
Your task board provides an interactive progress record for work required to complete the sprint. During the sprint, update the status of tasks and the remaining work for each task. Updating tasks daily or several times a week yields a smoother burndown chart.

Burndown chart
The sprint burndown chart reflects progress by your team in completing the work they estimated during planning. Use the burndown chart to help mitigate risk and check for scope creep throughout the sprint cycle.
On the burndown chart, the ideal trend line always indicates a steady burndown, while the blue area represents what's actually occurring. This area shows the buildup of work as team members add tasks and the reduction of work as team members complete their tasks.

Velocity and forecast tools
After several sprints, you can use the Velocity chart and Forecast tool to help estimate work your team can complete in future sprints.
Velocity chart
Velocity is a useful metric for gaining insight into how much work your team completes during a sprint cycle. Each team is associated with one velocity chart.
Select the Velocity chart on the Analytics tab of the team Backlog page. In the chart, light blue bars show the total amount of planned effort, based on story points or work item size, for a given sprint. The green areas indicate the total estimated effort for completed work items. The dark blue areas correspond to the estimated effort for items not yet completed.

Velocity varies depending on team capacity over sprints, but over time the Average Velocity should be reliable for forecasting against the full backlog. To get more reliable velocity metrics, minimize the variability of backlog item sizes, effort, and story points.
Forecast tool
The forecast tool helps determine how much work your team can complete within a sprint, given a specified team velocity. On the team Backlog page, select the View options icon and then set Forecasting to On.
On the forecast chart, set the velocity to different values to get an idea of how many and which items you can complete within a sprint. By setting a velocity, you can see which items are within scope for the set of sprints the team selected. In the following example, setting a velocity of 15 indicates that it takes three sprints to complete the work shown.

Sprint scope changes
There's no sprint scope change chart or widget, but the burndown chart shows the Total Scope Increase at upper right. You can also query for work items added to or removed from a sprint after its start.
Query for work items added or removed after sprint start
On the team backlog velocity chart or the velocity chart widget, select the Planned bar for the sprint you're interested in.
The Query Results page opens, showing the list of work items defined for the sprint at its start.
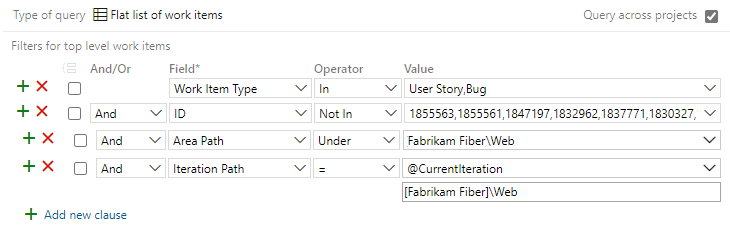
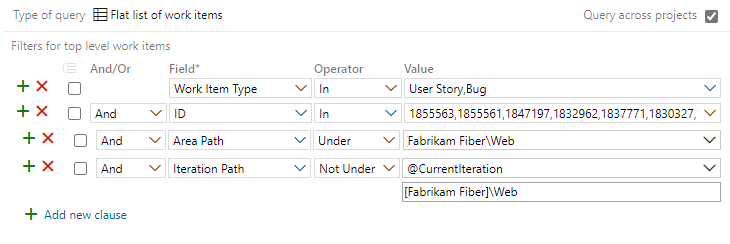
Select the Editor tab to edit the query, and on the Editor page, change the query as follows.
To list work items added to the sprint after its start:
- Change the operator for the ID field to Not In.
- Insert a clause at the top of the query to specify In for the Work Item Types you're interested in.
- Add an Under clause for the team's Area Path.
- Add an = clause for the sprint Iteration Path you're interested in.
The updated query should look similar to the following image:
To list work items moved out of the sprint after its start:
- Insert a clause at the top of the query to specify In for the Work Item Types you're interested in.
- Add an Under clause for the team's Area Path.
- Add a Not Under clause for the sprint Iteration Path you're interested in.
The updated query should look similar to the following image:
Select Column options and add Created Date as a column option, and sort by that field.
Run the queries to see the work items that were added to or removed from the sprint and when they were created.
For more information, see Query fields, operators, and macros in Azure Boards. For other options for determining changes to sprint scope, see Query by date or current iteration.