Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Azure DevOps Services | Azure DevOps Server | Azure DevOps Server 2022 | Azure DevOps Server 2020
In Azure Pipelines, you can allow users to customize pipeline execution by collecting their input with variables and parameters. However, accepting user input can also introduce security risks if not handled properly. In this article, you learn how to securely use variables and parameters in your pipeline.
This article is part of a series that helps you implement security measures for Azure Pipelines. For more information, see Secure Azure Pipelines.
Prerequisites
| Category | Requirements |
|---|---|
| Azure DevOps | - Implement recommendations in Make your Azure DevOps secure and Secure Azure Pipelines. - Basic knowledge of YAML and Azure Pipelines. For more information, see Create your first pipeline. |
| Permissions | - To modify pipelines permissions: Member of the Project Administrators group. - To modify organization permissions: Member of the Project Collection Administrators group. |
Variables
Variables are as a convenient way to gather user input in advance and facilitate data transfer between pipeline steps. However, variables that are defined in YAML tasks or scripts are read-write by default. Values set in upstream steps can modify downstream values unexpectedly.
For example, the following script snippet calls a variable called MyConfig.
msbuild.exe myproj.proj -property:Configuration=$(MyConfig)
If a preceding step set the MyConfig variable value to Debug & deltree /y c:, running this script deletes the contents of the build agent and could lead to unintended consequences. This example highlights the potential danger of such settings.
System variables like Build.SourcesDirectory and task output variables are always read-only. You can also designate a variable created in a script or YAML task as read-only by passing the isReadonly=true flag in its logging command.
In a YAML variable definition, you can specify a read-only variable by using the specific readonly key:
variables:
- name: myReadOnlyVar
value: myValue
readonly: true
Use particular caution with secret variables. The recommended methods for setting secret variables include using the UI, creating a variable group, or using a variable group sourced from Azure Key Vault. For more information, see Set secret variables.
Queue-time variables
When you define a variable in the Azure Pipelines UI, you can select whether to allow users to override the value during pipeline execution. Variables that allow users to set their value at queue time are called queue-time variables and can be defined only in the Azure Pipelines Variables UI.
In the Classic pipeline editor, you define queue-time variable by selecting the check box for Settable at queue time. In YAML pipelines, you designate them by selecting Let users override this value when running this pipeline.
Note
In a Release pipeline, select Settable at release time. For more information, see How can I edit variables at release time?
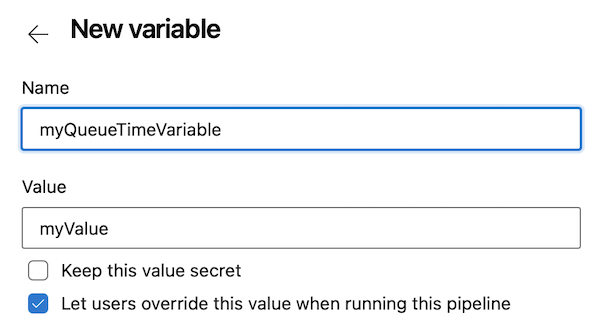
When a user manually runs the pipeline, they can select queue-time variables and change the values.

Users must have Edit queue build configuration permission on a pipeline to be able to define variables set at queue time.
Limit variables that can be set at queue time
The Azure Pipelines UI and the REST API that runs a pipeline provide ways for users to add new variables at queue time. This ability allows users to create variables that the pipeline author didn't define, to override system variables, and to set values for existing variables at queue time.
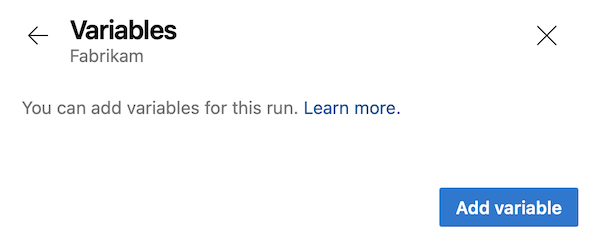
To avoid issues caused by these abilities, you can limit variables that can be set at queue time. You can enable the Limit variables that can be set at queue time setting so users can set only variables that are explicitly marked as Settable at queue time or Let users override this value when running this pipeline at queue time.
This setting can be applied at the organization and project levels.
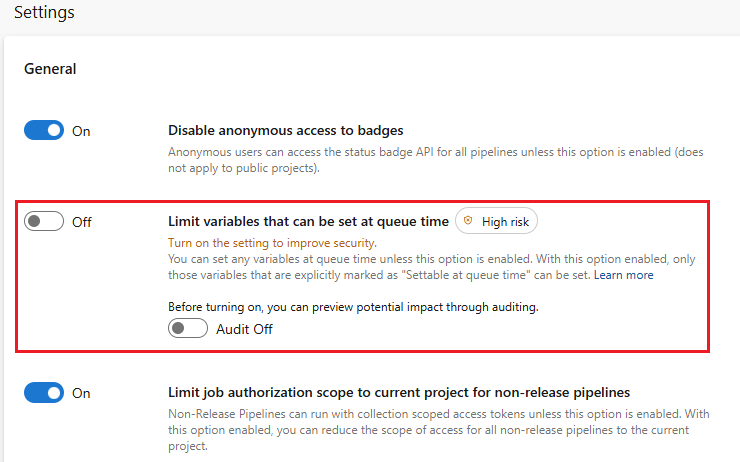
Project Collection Administrators can apply this setting at the organization level in Organization settings > Pipelines > Settings. When the setting is On, only variables that are explicitly marked as Settable at queue time can be set at queue time for all pipelines in all projects in the organization.

Project Administrators can apply this setting at the project level in Project settings > Pipelines > Settings. When the setting is On, only variables that are explicitly marked as Settable at queue time can be set at queue time for all pipelines in this project. If the setting isn't enabled at the organization level, it can be enabled or disabled for individual projects.
If the organization-level setting is enabled, it applies to all projects in the organization and can't be turned off at the project level.

The following example shows the variables for a Classic pipeline, with some of them marked Settable at queue time. The BuildPlatform variable can be set at queue time, but the BuildConfiguration can't.

When you run this pipeline, only the variables marked Settable at queue time are visible on the Variables screen to be selected.
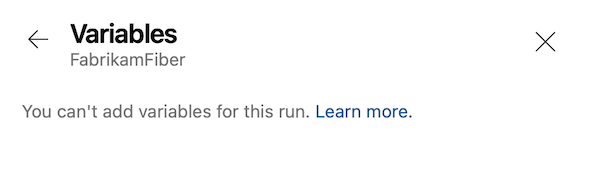
If Limit variables that can be set at queue time is enabled at the project or organization level, the Add variable button doesn't appear.

Using the Builds - Queue or the Runs - Run Pipeline APIs to queue a pipeline run and attempting to set the value of a variable not marked Settable at queue time fails with an error similar to the following:
{
"$id": "1",
"innerException": null,
"message": "You can't set the following variables (BuildConfiguration). If you want to be able to set these variables, then edit the pipeline and select Settable at queue time on the variables tab of the pipeline editor.",
"typeName": "Microsoft.Azure.Pipelines.WebApi.PipelineValidationException, Microsoft.Azure.Pipelines.WebApi",
"typeKey": "PipelineValidationException",
"errorCode": 0,
"eventId": 3000
}
Parameters
A running pipeline can't modify pipeline parameters, unlike variables. Parameters have data types such as number and string, and can be restricted to specific value subsets. This restriction is valuable when a user-configurable aspect of the pipeline should only accept values from a predefined list, ensuring that the pipeline doesn't accept arbitrary data.
Enable shell tasks arguments validation
Pipelines can reference tasks executed within the pipeline. Some tasks include an arguments parameter that allows users to specify more options for the task.
Applying the Enable shell tasks arguments validation setting validates argument parameters for built-in shell tasks to check for inputs that can inject commands into scripts. The check ensures that the shell correctly executes characters like semicolons, quotes, and parentheses in the following pipeline tasks:
- PowerShell
- BatchScript
- Bash
- Ssh
- AzureFileCopy
- WindowsMachineFileCopy
You can apply Enable shell tasks arguments validation at the organization level under Organization Settings > Pipelines > Settings or at the project level under Project settings > Pipelines > Settings. If the organization-level setting is enabled, it applies to all projects in the organization and can't be turned off at the project level.
When this setting is enabled, any validation issue related to an arguments parameter triggers the following error message:
Detected characters in arguments that may not be executed correctly by the shell. Please escape special characters using backtick (`).
To resolve the issue, adjust the argument by escaping special characters as indicated in the error message.