Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
The Python tool enables you to create customized code snippets as self-contained executable nodes in prompt flow. You can easily create Python tools, edit code, and verify results.
Inputs
| Name | Type | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| Code | string | Python code snippet | Yes |
| Inputs | - | List of tool function parameters and their assignments | - |
Types
| Type | Python example | Description |
|---|---|---|
| int | param: int | Integer type |
| bool | param: bool | Boolean type |
| string | param: str | String type |
| double | param: float | Double type |
| list | param: list or param: List[T] | List type |
| object | param: dict or param: Dict[K, V] | Object type |
| Connection | param: CustomConnection | Connection type is handled specially |
Parameters with the Connection type annotation are treated as connection inputs, which means:
- The prompt flow extension shows a selector to choose the connection.
- During execution, prompt flow tries to find the connection with the same name from the parameter value passed in.
Note
The Union[...] type annotation is supported only for the connection type, for example, param: Union[CustomConnection, OpenAIConnection].
Outputs
The outputs are the return value of the Python tool function.
Write with the Python tool
Use the following guidelines when writing with the Python tool.
Guidelines
Python tool code should consist of complete Python code, including any necessary module imports.
Python tool code must contain a function decorated with
@tool(tool function), which serves as the entry point for execution. Apply the@tooldecorator only once within the snippet.The following sample defines the Python tool
my_python_tool, which is decorated with@tool.Python tool function parameters must be assigned in the
Inputssection.The following sample defines the input
messageand assigns itworld.A Python tool function must have a return value.
The following sample returns a concatenated string.
Code
The following snippet shows the basic structure of a tool function. Prompt flow reads the function and extracts inputs from function parameters and type annotations.
from promptflow import tool
from promptflow.connections import CustomConnection
# The inputs section will change based on the arguments of the tool function, after you save the code
# Adding type to arguments and return value will help the system show the types properly
# Please update the function name/signature per need
@tool
def my_python_tool(message: str, my_conn: CustomConnection) -> str:
my_conn_dict = dict(my_conn)
# Do some function call with my_conn_dict...
return 'hello ' + message
Inputs
| Name | Type | Sample value in flow YAML | Value passed to function |
|---|---|---|---|
| message | string | world |
world |
| my_conn | CustomConnection |
my_conn |
CustomConnection object |
Prompt flow tries to find the connection named my_conn during execution.
Outputs
"hello world"
Call a reasoning model from the Python tool
If you need to call reasoning models that the LLM node doesn't support, you can use the Python tool to call the models directly. The following example shows how to call a reasoning model from the Python tool.
from promptflow import tool
from promptflow.connections import AzureOpenAIConnection
from openai import AzureOpenAI
@tool
def my_python_tool(
OpenAIConnection: AzureOpenAIConnection,
scope_reply: str
):
model_name = "o3-mini"
deployment = "o3-mini"
print(OpenAIConnection['api_base'])
endpoint = OpenAIConnection['api_base'] #"https://<your endpoint>.openai.azure.com/"
model_name = "o3-mini" #your model name
deployment = "o3-mini" #your deployment name
subscription_key = OpenAIConnection['api_key']
api_version = "2024-12-01-preview" #Supply an API version that supports reasoning models.
client = AzureOpenAI(
api_version=api_version,
azure_endpoint=endpoint,
api_key=subscription_key,
)
response = client.chat.completions.create(
messages=[
{
"role": "system",
"content": "You are a helpful assistant.",
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": "I am going to Paris, what should I see?",
}
],
max_completion_tokens=100000,
model=deployment
)
return response.choices[0].message.content
Custom connection in the Python tool
If you're developing a Python tool that requires calling external services with authentication, use the custom connection in prompt flow. You can use it to securely store the access key and then retrieve it in your Python code.
Create a custom connection
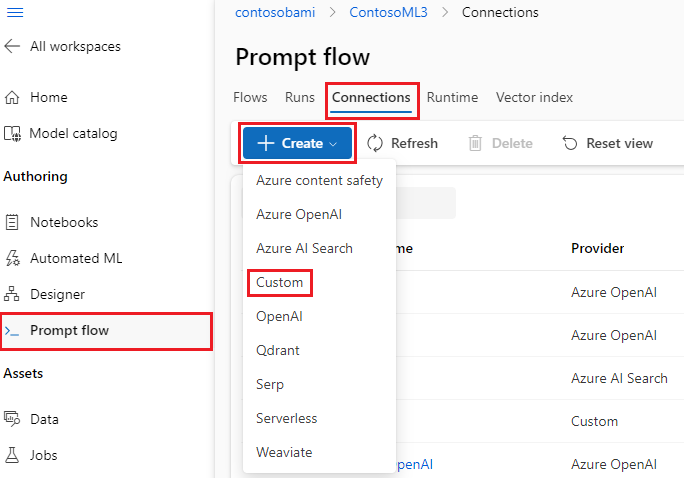
Create a custom connection that stores all your large language model API keys or other required credentials.
Go to prompt flow in your workspace, and then select the Connections tab.
Select Create > Custom.
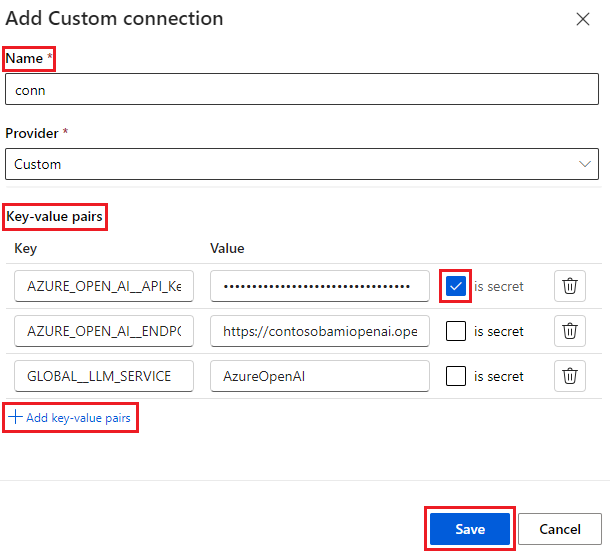
In the right pane, you can define your connection name. You can add multiple key-value pairs to store your credentials and keys by selecting Add key-value pairs.
Note
To set one key-value pair as secret, select the is secret checkbox. This option encrypts and stores your key value. Make sure at least one key-value pair is set as secret. Otherwise, the connection isn't created successfully.
Use a custom connection in Python
To use a custom connection in your Python code:
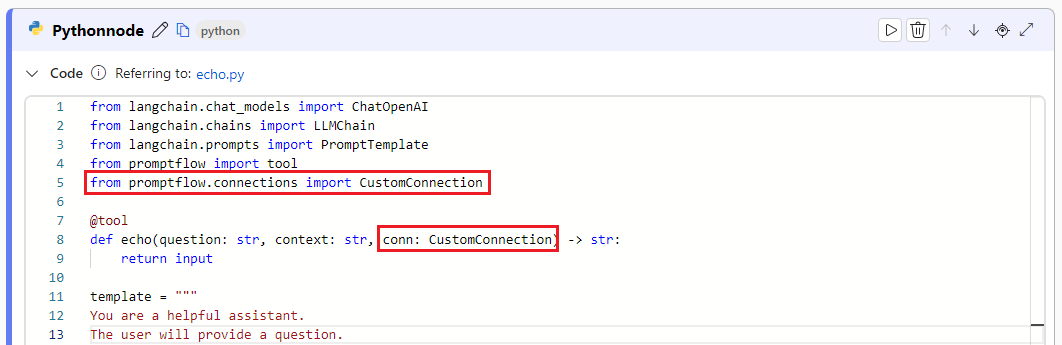
In the code section in your Python node, import the custom connection library
from promptflow.connections import CustomConnection. Define an input parameter of the typeCustomConnectionin the tool function.Parse the input to the input section, and then select your target custom connection in the Value dropdown.
For example:
from promptflow import tool
from promptflow.connections import CustomConnection
@tool
def my_python_tool(message: str, myconn: CustomConnection) -> str:
# Get authentication key-values from the custom connection
connection_key1_value = myconn.key1
connection_key2_value = myconn.key2