Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
In this Quickstart, you learn how to create a Microsoft Azure Red Hat OpenShift cluster using Azure CLI or the Azure portal. Azure Red Hat OpenShift is a managed OpenShift service that lets you deploy and manage clusters.
When you create the cluster, a service principal is created or you can use an existing service principal. A cluster that uses a service principal can't be migrated to use a managed identity. You need to create a new cluster that uses a managed identity on an Azure Red Hat OpenShift cluster. For more information, see Create an Azure Red Hat OpenShift cluster with managed identities (preview).
Prerequisites
Ensure you're using Azure CLI version 2.67.0 or higher. Use az --version to find the installed version of Azure CLI. If you need to install or upgrade, see Install Azure CLI.
Azure Red Hat OpenShift requires a minimum of 44 cores to create an OpenShift cluster. The default Azure resource quota for a new Azure subscription doesn't meet this requirement. To request an increase in your resource limit, see Increase VM-family vCPU quotas.
The 44 cores are used as follows:
- Bootstrap machine: 8 cores
- Control plane (master machines): 24 cores
- Compute (worker machines): 12 cores
When the installation is complete, the bootstrap machine is removed and your cluster uses a total of 36 cores. For more information, see Installing on Azure.
Run the following command to check your Azure subscription's quota for the Standard DSv5 virtual machine size that's the default virtual machine size for the az aro create command.
LOCATION=eastus
az vm list-usage --___location $LOCATION \
--query "[?contains(name.value, 'standardDSv5Family')]" \
--output table
Verify your permissions
In this article, you create a resource group that contains the virtual network for the cluster. You need Contributor and User Access Administrator permissions or Owner permissions, either directly on the virtual network or on the resource group or subscription containing it.
You also need sufficient Microsoft Entra permissions, either a member user of the tenant, or a guest assigned with role Application administrator, for the tooling to create an application and service principal on your behalf for the cluster. For more information, see Member and guests and Assign Microsoft Entra roles.
Register the resource providers
The following resource providers must be registered in your Azure subscription:
Microsoft.RedHatOpenShiftMicrosoft.ComputeMicrosoft.StorageMicrosoft.Authorization
If you have multiple Azure subscriptions, specify the relevant subscription ID:
az account set --subscription <SUBSCRIPTION ID>
To verify if a resource provider is registered, use the following command with the resource provider name. The command checks the Microsoft.RedHatOpenShift resource provider and returns a value of Registered or NotRegistered.
az provider list --query "[?namespace=='Microsoft.RedHatOpenShift'].registrationState" \
--output table
If you need to register resource providers, use the following commands:
Register the
Microsoft.RedHatOpenShiftresource provider:az provider register --namespace Microsoft.RedHatOpenShift --waitRegister the
Microsoft.Computeresource provider:az provider register --namespace Microsoft.Compute --waitRegister the
Microsoft.Storageresource provider:az provider register --namespace Microsoft.Storage --waitRegister the
Microsoft.Authorizationresource provider:az provider register --namespace Microsoft.Authorization --wait
Get a Red Hat pull secret (optional)
A Red Hat pull secret enables your cluster to access Red Hat container registries, along with other content like operators from OperatorHub. A pull secret doesn't change the cost of the Red Hat OpenShift license. This step is optional but recommended. For example, if you plan to use OpenShift Virtualization, include the pull secret in your cluster deployment so that operators like OpenShift Virtualization can be installed.
If you decide to add the pull secret later, see add or update your pull secret. The field cloud.openshift.com is removed from your secret even if your pull-secret contains that field. This field enables an extra monitoring feature, which sends data to RedHat and is thus disabled by default. To enable this feature, see Enabling remote health reporting.
Sign in to the Red Hat OpenShift cluster manager portal.
You need to sign in to your Red Hat account or create a new Red Hat account with your business email and accept the terms and conditions.
Select Download pull secret and download a pull secret to use with your cluster.
- Keep the saved
pull-secret.txtfile somewhere safe. The file is used in each cluster creation if you need to create a cluster that includes samples or operators for Red Hat or certified partners. - When running the
az aro createcommand, you can reference your pull secret using the--pull-secret @pull-secret.txtparameter. Executeaz aro createfrom the directory where you stored yourpull-secret.txtfile. Otherwise, replace@pull-secret.txtwith@/path/to/my/pull-secret.txt. - For an Azure portal cluster deployment, copy the pull secret and on the Authentication page, paste the pull secret into the Red Hat pull secret text box.
- If you copy your pull secret or reference it in other scripts, your pull secret should be formatted as a valid JSON string.
- Keep the saved
Prepare a custom ___domain for your cluster (optional)
When running the az aro create command, you can specify a custom ___domain for your cluster by using the --___domain foo.example.com parameter.
Note
Although adding a ___domain name is optional when you create a cluster through Azure CLI, a ___domain name, or a prefix used as part of the autogenerated DNS name for OpenShift console and API servers, is needed when adding a cluster through the portal. For more information, see this article's Azure portal tab.
If you provide a custom ___domain for your cluster, note the following points:
- After creating your cluster, you must create two DNS
Arecords in your DNS server for the--___domainspecified:- api - pointing to the API server IP address
- *.apps - pointing to the ingress IP address
- Retrieve these values by executing the following command after cluster creation:
az aro show -n -g --query '{api:apiserverProfile.ip, ingress:ingressProfiles[0].ip}'.
- The OpenShift console is available at a URL like
https://console-openshift-console.apps.example.com, instead of the built-in ___domainhttps://console-openshift-console.apps.<random>.<___location>.aroapp.io. - By default, OpenShift uses self-signed certificates for all of the routes created on custom domains
*.apps.example.com. If you choose to use custom DNS after connecting to the cluster, you need to follow the OpenShift documentation to configure a custom CA for your ingress controller and a custom CA for your API server.
Create a virtual network containing two empty subnets
Next, you create a virtual network containing two empty subnets. If you have existing virtual network that meets your needs, you can skip this step.
For information about networking and requirements, see Networking for Azure Red Hat OpenShift.
Set the following variables in the shell environment in which you execute the
azcommands.LOCATION=eastus # the ___location of your cluster RESOURCEGROUP=aro-rg # the name of the resource group where you want to create your cluster CLUSTER=cluster # the name of your cluster VIRTUALNETWORK=aro-vnet # the name of the virtual networkCreate a resource group.
An Azure resource group is a logical group in which Azure resources are deployed and managed. When you create a resource group, you're asked to specify a ___location. This ___location is where resource group metadata is stored, and it's also where your resources run in Azure if you don't specify another region during resource creation. Create a resource group using the az group create command.
Note
Azure Red Hat OpenShift isn't available in all regions where an Azure resource group can be created. See Available regions for information on where Azure Red Hat OpenShift is supported.
az group create \ --name $RESOURCEGROUP \ --___location $LOCATIONThe following example output shows the resource group created successfully:
{ "id": "/subscriptions/<guid>/resourceGroups/aro-rg", "___location": "eastus", "name": "aro-rg", "properties": { "provisioningState": "Succeeded" }, "type": "Microsoft.Resources/resourceGroups" }Create a virtual network.
Azure Red Hat OpenShift clusters running OpenShift 4 require a virtual network with two empty subnets, for the master and worker nodes. You can either create a new virtual network for this cluster, or use an existing virtual network.
Create a new virtual network in the same resource group you created earlier:
az network vnet create \ --resource-group $RESOURCEGROUP \ --name $VIRTUALNETWORK \ --address-prefixes 10.0.0.0/22The following example output shows the virtual network created successfully:
{ "newVNet": { "addressSpace": { "addressPrefixes": [ "10.0.0.0/22" ] }, "dhcpOptions": { "dnsServers": [] }, "id": "/subscriptions/<guid>/resourceGroups/aro-rg/providers/Microsoft.Network/virtualNetworks/aro-vnet", "___location": "eastus", "name": "aro-vnet", "provisioningState": "Succeeded", "resourceGroup": "aro-rg", "type": "Microsoft.Network/virtualNetworks" } }Add an empty subnet for the master nodes.
az network vnet subnet create \ --resource-group $RESOURCEGROUP \ --vnet-name $VIRTUALNETWORK \ --name master-subnet \ --address-prefixes 10.0.0.0/23Add an empty subnet for the worker nodes.
az network vnet subnet create \ --resource-group $RESOURCEGROUP \ --vnet-name $VIRTUALNETWORK \ --name worker-subnet \ --address-prefixes 10.0.2.0/23
Create the cluster
To create a cluster, run the following command. If you choose to use either of the following options, modify the command accordingly:
- Optionally, you can pass your Red Hat pull secret, which enables your cluster to access Red Hat container registries along with other content. Add the
--pull-secret @pull-secret.txtargument to your command. - Optionally, you can use a custom ___domain. Add the
--___domain foo.example.comargument to your command, replacingfoo.example.comwith your own custom ___domain. - The default master virtual machine size is
Standard D8s_v5. If you need a different virtual machine size, use the--master-vm-sizeparameter. For example,--master-vm-size Standard_D8s_v3. - The default worker virtual machine size is
Standard D4s_v5. If you need a different virtual machine size, use the--worker-vm-sizeparameter. For example,--worker-vm-size Standard_D4s_v3. - The cluster is created with an OpenShift Container Platform version with install availability. To ensure your cluster is created with the latest available install version see select a different version. In the
--versionparameter, replace<x.y.z>with a specific version like4.17.27. - For more information about the command to create the cluster, see az aro create.
Note
The maximum number of worker nodes definable at creation time is 50. You can scale out up to 250 nodes after the cluster is created.
az aro create \
--resource-group $RESOURCEGROUP \
--name $CLUSTER \
--vnet $VIRTUALNETWORK \
--master-subnet master-subnet \
--worker-subnet worker-subnet \
--version <x.y.z>
After you run the az aro create command, it takes about 45 minutes to create the cluster.
Large scale clusters
If you need to deploy an Azure Red Hat OpenShift cluster with more than 100 worker nodes, see Deploy a large Azure Red Hat OpenShift cluster.
Select a different version
Use the following command to list the versions available for the ___location where you want to deploy a cluster.
az aro get-versions --___location $LOCATION --output table
Version
---------
4.14.38
4.14.51
4.15.35
4.15.49
4.16.30
4.16.39
4.17.27
After you decide which version you want to install, specify it in the az aro create command's --version parameter.
Prerequisites
Sign in to the Azure portal.
Register the Microsoft.RedHatOpenShift resource provider. For instructions on registering resource providers using Azure portal, see Register resource provider. You should also verify that Microsoft.Compute, Microsoft.Storage, and Microsoft.Authorization are registered.
Azure Red Hat OpenShift requires a minimum of 44 cores to create an OpenShift cluster. The default Azure resource quota for a new Azure subscription doesn't meet this requirement. To request an increase in your resource limit, see Increase VM-family vCPU quotas.
The 44 cores are used as follows:
- Bootstrap machine: 8 cores
- Control plane (master machines): 24 cores
- Compute (worker machines): 12 cores
When the installation is complete, the bootstrap machine is removed and your cluster uses a total of 36 cores. For more information, see Installing on Azure.
In Azure portal, the Standard DSv3 virtual machine size is the default size to create and run an OpenShift cluster.
Get a Red Hat pull secret (optional)
A Red Hat pull secret enables your cluster to access Red Hat container registries, along with other content like operators from OperatorHub. A pull secret doesn't change the cost of the Red Hat OpenShift license. This step is optional but recommended. For example, if you plan to use OpenShift Virtualization, include the pull secret in your cluster deployment so that operators like OpenShift Virtualization can be installed.
If you decide to add the pull secret later, see add or update your pull secret. The field cloud.openshift.com is removed from your secret even if your pull-secret contains that field. This field enables an extra monitoring feature, which sends data to RedHat and is thus disabled by default. To enable this feature, see Enabling remote health reporting.
Sign in to the Red Hat OpenShift cluster manager portal.
You need to sign in to your Red Hat account or create a new Red Hat account with your business email and accept the terms and conditions.
Select Download pull secret and download a pull secret to use with your cluster.
- Keep the saved
pull-secret.txtfile somewhere safe. The file is used in each cluster creation if you need to create a cluster that includes samples or operators for Red Hat or certified partners. - When running the
az aro createcommand, you can reference your pull secret using the--pull-secret @pull-secret.txtparameter. Executeaz aro createfrom the directory where you stored yourpull-secret.txtfile. Otherwise, replace@pull-secret.txtwith@/path/to/my/pull-secret.txt. - For an Azure portal cluster deployment, copy the pull secret and on the Authentication page, paste the pull secret into the Red Hat pull secret text box.
- If you copy your pull secret or reference it in other scripts, your pull secret should be formatted as a valid JSON string.
- Keep the saved
Create an Azure Red Hat OpenShift cluster
On the Azure portal menu or from the Home page, select All Services under three horizontal bars on the top left hand page.
Search for and select Azure Red Hat OpenShift clusters.
Select Create.
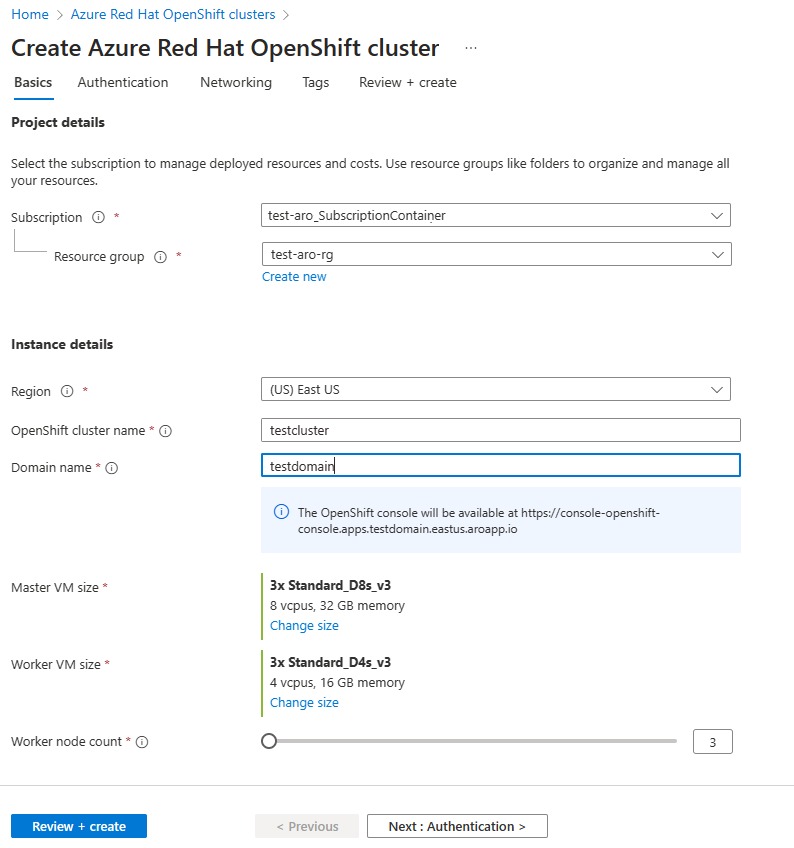
On the Basics tab, configure the following options:
- Project details:
- Select an Azure Subscription.
- Select or create an Azure Resource group, like test-aro-rg.
- Instance details:
- Select a Region for the Azure Red Hat OpenShift cluster.
- Enter an OpenShift cluster name, like
testcluster. - Enter a Domain name, like
testdomain. - Select Master VM Size and Worker VM Size.
- Select Worker node count (the number of worker nodes to create).
Note
The Domain name field is prepopulated with a random string. You can either specify a ___domain name like example.com or a string/prefix like abc that's used as part of the autogenerated DNS name for OpenShift console and API servers. This prefix is also used as part of the name of the resource group that is created to host the cluster VMs if a resource group name isn't specified.
- Project details:
On the Authentication tab, complete the following sections.
Under Service principal information, select either Create new or Existing. If you choose to use an existing service principal, enter the following information:
- Service principal client ID is your
appId. - Service principal client secret is the service principal's decrypted secret value.
Note
If you need to create a service principal, see Creating and using a service principal with an Azure Red Hat OpenShift cluster.
Under Pull secret, enter the Red Hat pull secret (your cluster's pull secret's decrypted value). If you don't have a pull secret, leave this field blank.
- Service principal client ID is your
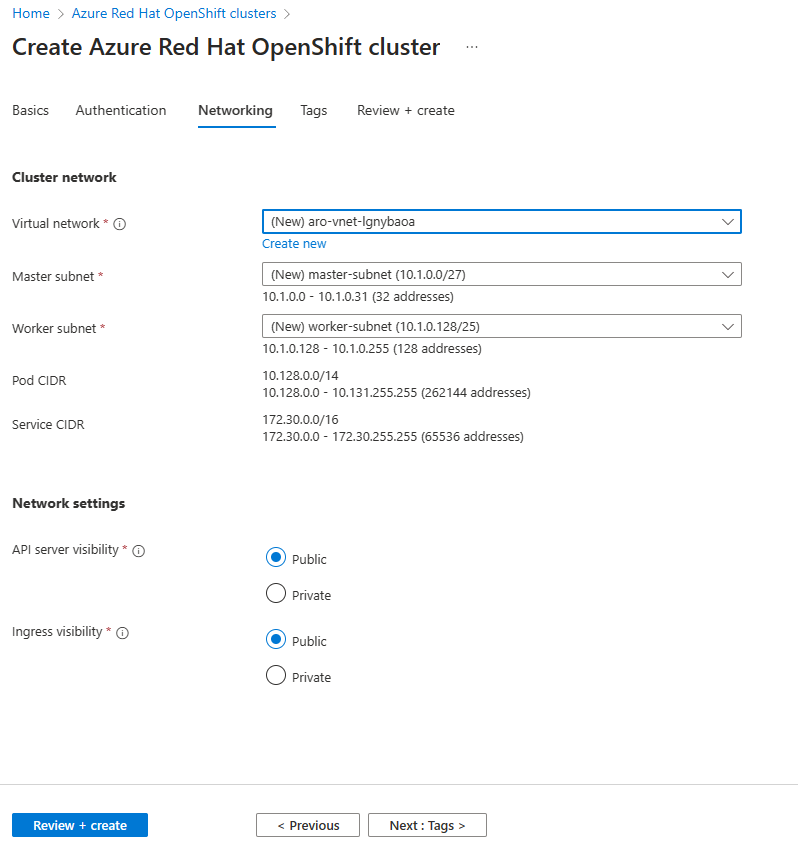
On the Networking tab, configure the required options.
Note
Azure Red Hat OpenShift clusters running OpenShift 4 require a virtual network with two empty subnets: one for the control plane and one for worker nodes.
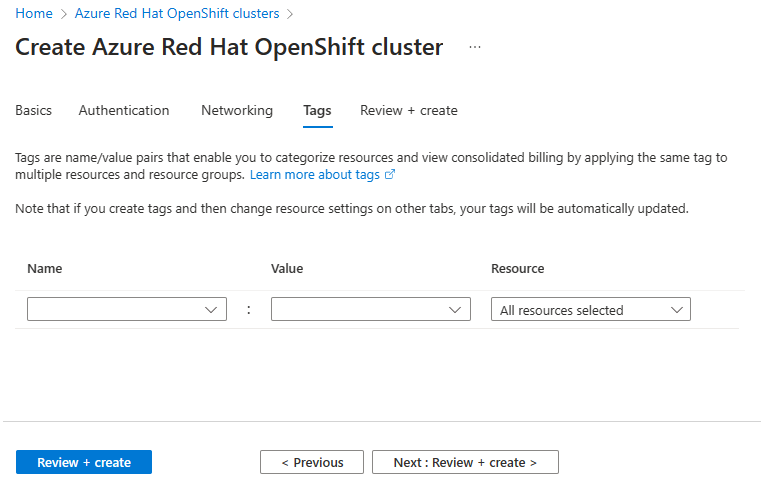
On the Tags tab, add tags to organize your resources.
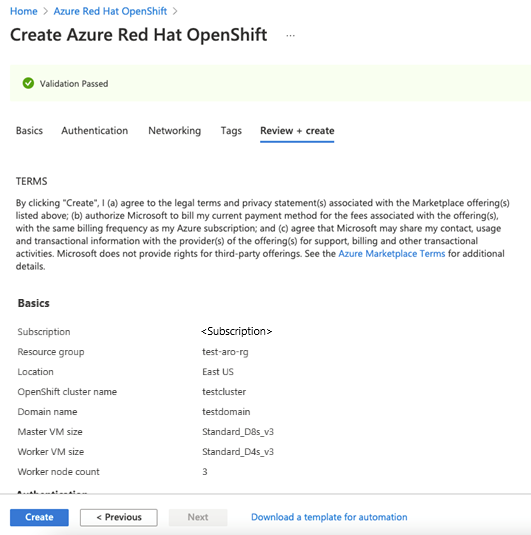
Check Review + create and then Create when validation completes.
It takes about 45 minutes to create the Azure Red Hat OpenShift cluster. When your deployment is complete, navigate to your resource by either:
- Select Go to resource.
- Browse to the Azure Red Hat OpenShift cluster resource group and select the Azure Red Hat OpenShift resource.