Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This article describes the configurations available for your Azure Managed Redis instances.
Configure Azure Managed Redis settings
You can view and configure the following settings using the Resource Menu.
- Overview
- Activity log
- Access control (IAM)
- Tags
- Diagnose and solve problems
- Settings
- Administration
- Monitoring
- Automation
- Help
Overview
The Overview section provides you with basic information about your instance, such as name, endpoint, pricing tier, modules, geo-replication status, and selected cache metrics.
Activity log
Select Activity log to view actions done to your cache. You can also use filtering to expand this view to include other resources. For more information on working with audit logs, see Audit operations with Resource Manager. For more information on monitoring the activity log, see Activity log.
Access control (IAM)
The Access control (IAM) section provides support for Azure role-based access control (Azure RBAC) in the Azure portal. This configuration helps organizations meet their access management requirements simply and precisely. For more information, see Azure role-based access control in the Azure portal.
Tags
The Tags section helps you organize your resources. For more information, see Using tags to organize your Azure resources.
Diagnose and solve problems
Select Diagnose and solve problems to be provided with common issues and strategies for resolving them.
Settings
The Settings section allows you to access and configure the following settings for your cache.
- Authentication
- Advanced settings
- Data persistence (preview)
- Encryption
- Active geo-replication
- Scale
- Properties
- Locks
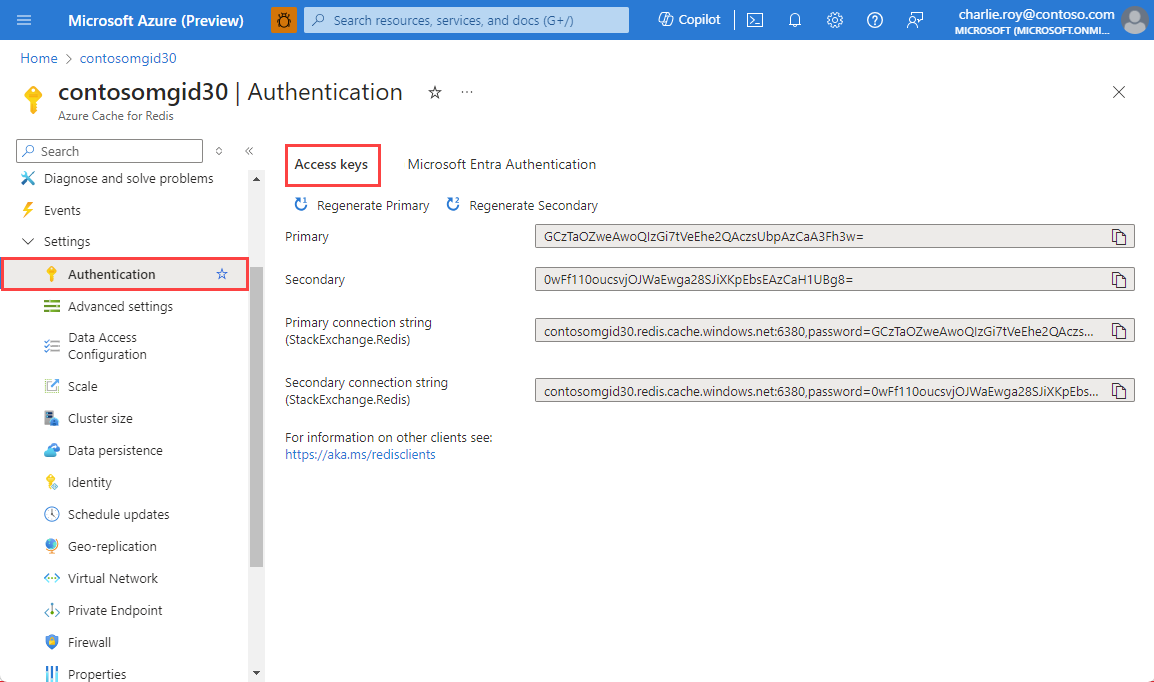
Authentication
You have two options for authentication: access keys and Microsoft Entra Authentication. Using Microsoft Entra Authentication is recommended because it's more secure.
Select Access keys to view or regenerate the access keys for your cache. These keys are used by the clients connecting to your cache.
Advanced settings
The following properties are set:
- Non-TLS access only
- Eviction Policy
- Defer Redis DB version updates
Data persistence (preview)
Use Data persistence to enable, disable, or configure data persistence for your Redis cache. Azures Managed Redis offers Redis persistence using either RDB persistence or AOF persistence.
For more information, see Configure data persistence for an Azure Managed Redis instance.
Encryption
Select Encryption to encrypt any data stored on disk, such as data persistence files or files being exported from the instance. For more information, see Configure disk encryption for Azure Managed Redis instances using customer managed keys
Active geo-replication
Active geo-replication, on the Resource menu, provides a mechanism for linking up to five Azure Managed Redis instances in an active-active configuration. This functionality can be used to replicate a cache across Azure regions, providing greater data durability and availability. For more information, see Configure active geo-replication for Azure Managed Redis instances
Scale (preview)
Select Scale to view or change the size and performance tier of your Redis instance. For more information on scaling, see How to Scale Azure Managed Redis.
Properties
Select Properties to view information about your instance, including the endpoint, Redis DB version, and clustering policy.
Locks
The Locks section allows you to lock a subscription, resource group, or resource to prevent other users in your organization from accidentally deleting or modifying critical resources. For more information, see Lock resources with Azure Resource Manager.
Administration
The Administration section allows you to access and configure the following settings for your Redis instance:
Import/Export
Import/Export is an Azure Managed Redis data management operation that allows you to import and export data to/from the Redis instance. You can import and export a Redis Database (RDB) snapshot to/from an Azure Storage Account. Use Import/Export to migrate between different Azure Managed Redis instances or populate the cache with data before use.
You can use import with Redis-compatible RDB files from any Redis server running in virtually any cloud or environment including:
- Redis running on VMs or containers
- cloud providers such as Amazon Web Services or others
Importing data is an easy way to create a cache with prepopulated data. During the import process, Azure Managed Redis loads the RDB files from Azure storage into memory, and then inserts the keys into the cache.
Export allows you to export the data stored in Azure Managed Redis to Redis compatible RDB files. You can use this feature to move data from one Azure Managed Redis instance to another or to another Redis server.
During the export process, a temporary file is created on the VM that hosts the Azure Managed Redis instance. The temporary file is uploaded to the designated storage account. When the export operation completes with either a status of success or failure, the temporary file is deleted.
For more information and instructions, see Import and Export data in Azure Managed Redis.
Private endpoint
The Private Endpoint section allows you to configure the private endpoint settings for your instance. We recommend using private endpoints for all production workloads.
For more information, see Azure Cache for Redis with Azure Private Link.
Monitoring
The Monitoring section allows you to configure diagnostics and monitoring for your Azure Managed Redis instance.
- For more information on Azure Managed Redis monitoring and diagnostics, see Monitor Azure Managed Redis.
- For a list of metrics used in Azure Managed Redis, see Azure Managed Redis monitoring data reference.
Alerts
Select Alerts to configure alerts based on Azure Managed Redis metrics. For more information, see Create alerts.
Metrics
Select Metrics to create your own custom chart to track the metrics you want to see for your cache. For more information, see Create your own metrics.
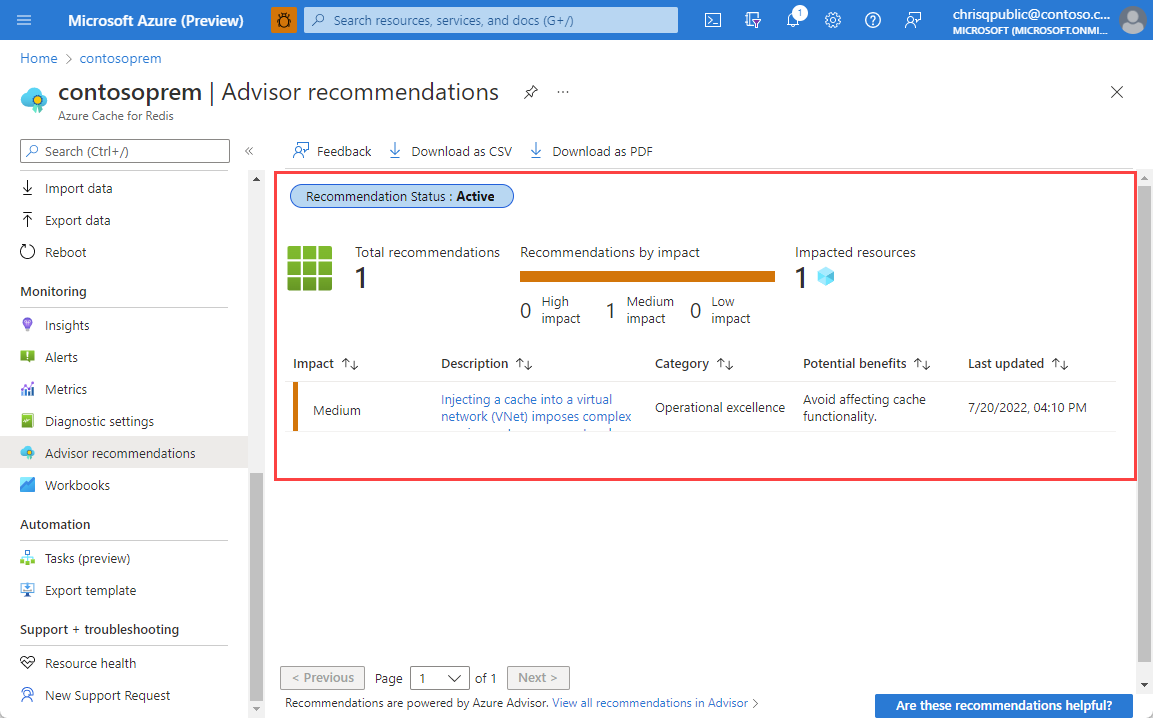
Advisor recommendations
The Advisor recommendations displays recommendations for your cache. During normal operations, no recommendations are displayed.
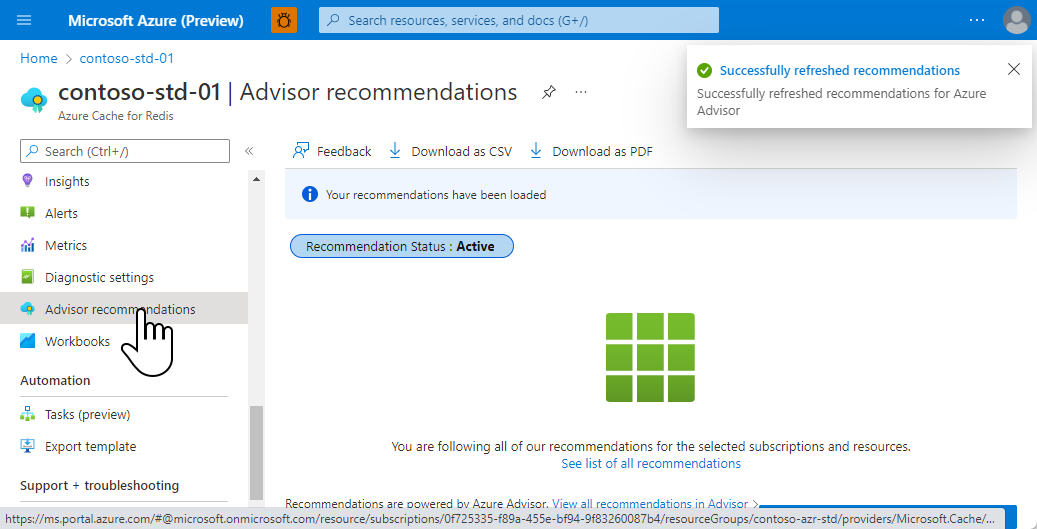
If any conditions occur during the operations of your cache such as imminent changes, high memory usage, network bandwidth, or server load, an alert is displayed in the Overview of the Resource menu.
Further information can be found on the Recommendations in the working pane of the Azure portal.
Diagnostic Settings Metrics
By default, cache metrics in Azure Monitor are stored for 30 days and then deleted.
To persist your cache metrics for longer than 30 days, select Diagnostics Settings - Metrics to configure the storage account used to store cache diagnostics.
Note
In addition to archiving your cache metrics to storage, you can also stream them to an Event hub or send them to Azure Monitor logs.
Diagnostic Settings Auditing
Use Diagnostic Settings - Auditing to log connections made to the Azure Managed Redis instance, including both successful and unsuccessful connection attempts. For more information, see Monitor Azure Managed Redis data using diagnostic settings
Automation
Azure Automation delivers a cloud-based automation, operating system updates, and configuration service that supports consistent management across your Azure and non-Azure environments.
Tasks
Select Tasks to help you manage Azure Managed Redis resources more easily. These tasks vary in number and availability, based on the resource type. Presently, you can only use the Send monthly cost for resource template to create a task while in preview.
For more information, see Manage Azure resources and monitor costs by creating automation tasks.
Export template
Select Export template to build and export a template of your deployed resources for future deployments. For more information about working with templates, see Deploy resources with Azure Resource Manager templates.
Help
The settings in the Help section provide you with options for resolving issues with your cache.
Resource health
Resource health watches your resource and tells you if it's running as expected. Resource health isn't yet supported for Azure Managed Redis. For more information about the Azure Resource health service, see Azure Resource health overview.
Support and Troubleshooting
Select Support + Troubleshooting to open a support request for your cache.
Other configuration information
Here's some additional information about Azure Managed Redis caches.
Databases
Currently, Azure Managed Redis only supports a single database per instance.
Maximum number of clients
The maxclients property is different for each Azure Managed Redis SKU.
See the Azure Managed Redis pricing page for more information about the connection limits per SKU.
Note
Each cache size allows up to some number connections, but each connection adds overhead. Examples of such overhead include CPU and memory usage due to TLS/SSL encryption. The maximum connection limit for a cache size assumes a lightly loaded cache. If the load from connection overhead plus the load from client operations exceeds the system's capacity, the cache might encounter capacity issues even without exceeding the connection limit for the current cache size.
Redis commands not supported in Azure Managed Redis
Microsoft manages the configuration and management of Azure Managed Redis instances, which disables several commands in order to ensure safe and consistent operation of the service.
If you try to invoke a disabled command, you receive an error message similar to "(error) ERR unknown command".
Blocked commands include:
- BGREWRITEAOF
- BGSAVE
- CLUSTER - Cluster write commands are disabled, but read-only cluster commands are permitted.
- MODULE LOAD
- MOVE
- PSYNC
- REPLICAOF
- REPLCONF - Azure Managed Redis instances don't allow customers to add external replicas. Normally, only servers send this command.
- SAVE
- SHUTDOWN
- SELECT
- SYNC
For a full list of blocked commands, see Compatibility with Redis Community Edition commands
For cache instances using active geo-replication, the following commands are also blocked to prevent accidental data loss:
- FLUSHALL
- FLUSHDB
Instead, use the control plane flush operation through the portal, PowerShell, or CLI.
