Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This quickstart shows you how to use an Azure Resource Manager template (ARM template) to deploy Azure Route Server into a new or existing virtual network. Azure Route Server enables dynamic routing between your virtual network and network virtual appliances through BGP peering, automatically managing route exchanges in your network infrastructure.
By completing this quickstart, you'll have a functioning Route Server deployed with the necessary network infrastructure and ready for BGP peering configuration.
An Azure Resource Manager template is a JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) file that defines the infrastructure and configuration for your project. The template uses declarative syntax. You describe your intended deployment without writing the sequence of programming commands to create the deployment.
If your environment meets the prerequisites and you're familiar with using ARM templates, select the Deploy to Azure button to open the template in the Azure portal.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, ensure you have the following requirements:
- An Azure account with an active subscription. Create an account for free.
- Familiarity with Azure Route Server service limits.
Review the template
The template used in this quickstart is from Azure Quickstart Templates. This ARM template deploys a complete Route Server environment including the virtual network infrastructure and BGP peering configuration.
The template creates the following resources:
- Azure Route Server in a new or existing virtual network
- Dedicated subnet named RouteServerSubnet to host the Route Server
- BGP peering configuration with specified Peer ASN and Peer IP
{
"$schema": "https://schema.management.azure.com/schemas/2019-04-01/deploymentTemplate.json#",
"contentVersion": "1.0.0.0",
"metadata": {
"_generator": {
"name": "bicep",
"version": "0.5.6.12127",
"templateHash": "3572840517141664306"
}
},
"parameters": {
"vnetName": {
"type": "string",
"defaultValue": "routeservervnet",
"metadata": {
"description": "Name of new or existing vnet to which Azure Route Server should be deployed."
}
},
"vnetIpPrefix": {
"type": "string",
"defaultValue": "10.1.0.0/16",
"metadata": {
"description": "IP prefix for available addresses in vnet address space."
}
},
"vnetNew_or_Existing": {
"type": "string",
"defaultValue": "New",
"allowedValues": [
"New",
"Existing"
],
"metadata": {
"description": "Specify whether to provision new vnet or deploy to existing vnet."
}
},
"routeServerSubnetIpPrefix": {
"type": "string",
"defaultValue": "10.1.1.0/26",
"metadata": {
"description": "Route Server subnet IP prefix MUST be within vnet IP prefix address space."
}
},
"publicIpNew_or_Existing": {
"type": "string",
"defaultValue": "New",
"allowedValues": [
"New",
"Existing"
],
"metadata": {
"description": "Specify whether to provision new standard public IP or deploy using existing standard public IP."
}
},
"publicIpName": {
"type": "string",
"defaultValue": "routeserverpip",
"metadata": {
"description": "Name of the standard Public IP used for the Route Server"
}
},
"firstRouteServerName": {
"type": "string",
"defaultValue": "routeserver",
"metadata": {
"description": "Name of Route Server."
}
},
"routeServerBgpConnectionName": {
"type": "string",
"defaultValue": "conn1",
"metadata": {
"description": "Name of BGP connection."
}
},
"peerAsn": {
"type": "int",
"defaultValue": 65002,
"metadata": {
"description": "Peer ASN connecting to."
}
},
"peerIp": {
"type": "string",
"defaultValue": "10.0.1.4",
"metadata": {
"description": "Peer IP connecting to."
}
},
"___location": {
"type": "string",
"defaultValue": "[resourceGroup().___location]",
"metadata": {
"description": "Azure region for Route Server and virtual network."
}
}
},
"variables": {
"ipconfigName": "ipconfig1",
"routeServerSubnetName": "RouteServerSubnet"
},
"resources": [
{
"condition": "[equals(parameters('vnetNew_or_Existing'), 'New')]",
"type": "Microsoft.Network/virtualNetworks",
"apiVersion": "2020-05-01",
"name": "[parameters('vnetName')]",
"___location": "[parameters('___location')]",
"properties": {
"addressSpace": {
"addressPrefixes": [
"[parameters('vnetIpPrefix')]"
]
}
}
},
{
"type": "Microsoft.Network/virtualNetworks/subnets",
"apiVersion": "2020-05-01",
"name": "[format('{0}/{1}', parameters('vnetName'), variables('routeServerSubnetName'))]",
"properties": {
"addressPrefix": "[parameters('routeServerSubnetIpPrefix')]"
},
"dependsOn": [
"[resourceId('Microsoft.Network/virtualNetworks', parameters('vnetName'))]"
]
},
{
"condition": "[equals(parameters('publicIpNew_or_Existing'), 'New')]",
"type": "Microsoft.Network/publicIPAddresses",
"apiVersion": "2020-05-01",
"name": "[parameters('publicIpName')]",
"___location": "[parameters('___location')]",
"sku": {
"name": "Standard"
},
"properties": {
"publicIPAllocationMethod": "Static",
"publicIPAddressVersion": "IPv4",
"idleTimeoutInMinutes": 4
}
},
{
"type": "Microsoft.Network/virtualHubs",
"apiVersion": "2020-06-01",
"name": "[parameters('firstRouteServerName')]",
"___location": "[parameters('___location')]",
"properties": {
"sku": "Standard"
}
},
{
"type": "Microsoft.Network/virtualHubs/ipConfigurations",
"apiVersion": "2020-06-01",
"name": "[format('{0}/{1}', parameters('firstRouteServerName'), variables('ipconfigName'))]",
"properties": {
"subnet": {
"id": "[resourceId('Microsoft.Network/virtualNetworks/subnets', parameters('vnetName'), variables('routeServerSubnetName'))]"
},
"publicIPAddress": {
"id": "[resourceId('Microsoft.Network/publicIPAddresses', parameters('publicIpName'))]"
}
},
"dependsOn": [
"[resourceId('Microsoft.Network/virtualHubs', parameters('firstRouteServerName'))]",
"[resourceId('Microsoft.Network/publicIPAddresses', parameters('publicIpName'))]",
"[resourceId('Microsoft.Network/virtualNetworks/subnets', parameters('vnetName'), variables('routeServerSubnetName'))]"
]
},
{
"type": "Microsoft.Network/virtualHubs/bgpConnections",
"apiVersion": "2020-06-01",
"name": "[format('{0}/{1}', parameters('firstRouteServerName'), parameters('routeServerBgpConnectionName'))]",
"properties": {
"peerAsn": "[parameters('peerAsn')]",
"peerIp": "[parameters('peerIp')]"
},
"dependsOn": [
"[resourceId('Microsoft.Network/virtualHubs', parameters('firstRouteServerName'))]",
"[resourceId('Microsoft.Network/virtualHubs/ipConfigurations', parameters('firstRouteServerName'), variables('ipconfigName'))]"
]
}
]
}
Template resources
The following Azure resources are defined in the template:
- Microsoft.Network/virtualNetworks - Virtual network to host the Route Server
- Microsoft.Network/virtualNetworks/subnets - Two subnets, including the required RouteServerSubnet
- Microsoft.Network/virtualHubs - Route Server deployment resource
- Microsoft.Network/virtualHubs/ipConfigurations - IP configuration for Route Server
- Microsoft.Network/virtualHubs/bgpConnections - BGP peering configuration with Peer ASN and Peer IP
To find more templates related to Azure networking, see Azure Quickstart Templates.
Deploy the template
You can deploy the template using Azure PowerShell through Azure Cloud Shell or your local PowerShell environment.
Select Open Cloud Shell from the following code block to open Azure Cloud Shell, and then follow the instructions to sign in to Azure:
$projectName = Read-Host -Prompt "Enter a project name that is used for generating resource names" $___location = Read-Host -Prompt "Enter the ___location (i.e. centralus)" $templateUri = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure/azure-quickstart-templates/master/quickstarts/microsoft.network/route-server/azuredeploy.json" $resourceGroupName = "${projectName}rg" New-AzResourceGroup -Name $resourceGroupName -Location "$___location" New-AzResourceGroupDeployment -ResourceGroupName $resourceGroupName -TemplateUri $templateUri Read-Host -Prompt "Press [ENTER] to continue ..."Wait until you see the prompt from the console.
Select Copy from the previous code block to copy the PowerShell script.
Right-click the shell console pane and then select Paste.
Enter the values when prompted:
- Project name: Used for generating resource names (the resource group name will be the project name with rg appended)
- Location: Azure region where resources will be deployed
The deployment takes approximately 20 minutes to complete. When finished, the output should be similar to:

Azure PowerShell is used to deploy the template in this example. You can also use the Azure portal, Azure CLI, and REST API for template deployment. To learn about other deployment methods, see Deploy templates.
Validate the deployment
After the template deployment completes, verify that the Route Server was created successfully.
Verify resources in the Azure portal
Sign in to the Azure portal.
Select Resource groups from the left pane.
Select the resource group that you created in the previous section. The default resource group name is the project name with rg appended.
The resource group should contain the virtual network and associated resources:
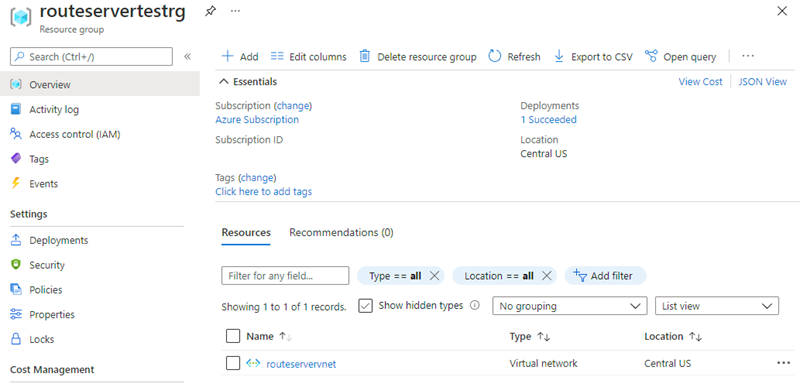
Verify Route Server deployment
From the Azure portal, navigate to your resource group and select the Route Server resource.
On the Route Server overview page, verify the following:
- Status shows as "Succeeded"
- BGP ASN displays the configured autonomous system number
- Routing State shows as "Provisioned"

Clean up resources
When you no longer need the Route Server and associated resources, delete the resource group to remove the Route Server and all related resources.
To delete the resource group, use the Remove-AzResourceGroup cmdlet:
Remove-AzResourceGroup -Name <your resource group name>
Next step
Now that you've deployed a Route Server using an ARM template, learn more about Route Server capabilities:
