Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Although Azure AI Search is a single-region service, you can achieve higher availability and resiliency by deploying multiple search services with identical configurations and content across multiple regions.
This article describes the components of a multi-region solution, which relies on your custom script or code to handle failover if a service becomes unavailable.
For more information about the reliability features of Azure AI Search, including intra-regional resiliency via availability zones, see Reliability in Azure AI Search.
Why use multiple regions?
If you need two or more search services, creating them in different regions can meet the following operational requirements:
Resiliency to region outages. If there's an outage, Azure AI Search doesn't provide instant failover to another region.
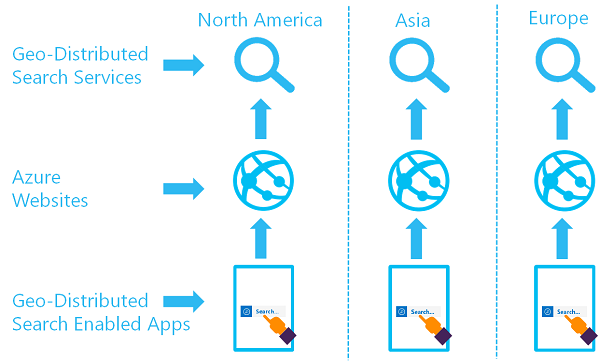
Fast performance for a globally distributed application. If indexing and query requests come from around the world, users who are closest to the host data center experience faster performance. Creating more services in regions with close proximity to these users can equalize performance for everyone.
Multi-region architecture
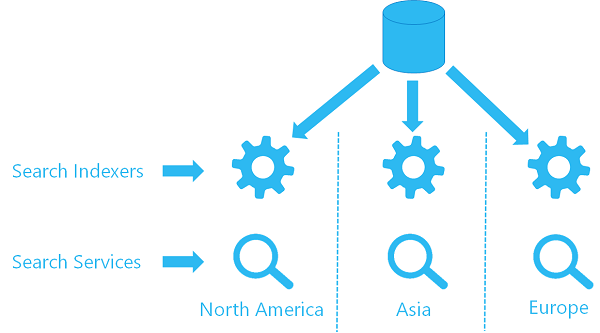
In a multi-region setup, two or more search services are located in different regions and have synchronized indexes. Users are automatically routed to the service with the lowest latency.
Azure AI Search doesn't provide an automated method of index replication across regions. However, you can synchronize data using push or pull model indexing, both of which are described in the following section. You can also add Azure Traffic Manager or another load balancer for request redirection.
The following diagram illustrates a geo-distributed set of search services:
Tip
For a complete implementation, see the Bicep sample on GitHub. The sample deploys a fully configured, multi-region search solution that can be modified to your regions and indexing strategies.
Data synchronization
To synchronize two or more distinct search services, you can either:
- Push content into an index using Documents - Index (REST API) or an equivalent API in the Azure SDKs.
- Pull content into an index using an indexer.
If you use the REST APIs to push content into your index, you can synchronize multiple search services by sending updates to each service whenever changes occur. Ensure that your code handles cases in which an update fails for one service but succeeds for other services.
Data residency
When you create multiple search services in different regions, your content is stored in the region you chose for each service.
Azure AI Search doesn't store data outside of your specified region without your authorization. Authorization is implicit when you use features that write to Azure Storage, for which you provide a storage account in your preferred region. These features include:
If your search service and storage account are in the same region, network traffic uses private IP addresses over the Microsoft backbone network, so you can't configure IP firewalls or private endpoints for network security. As an alternative, use the trusted service exception.
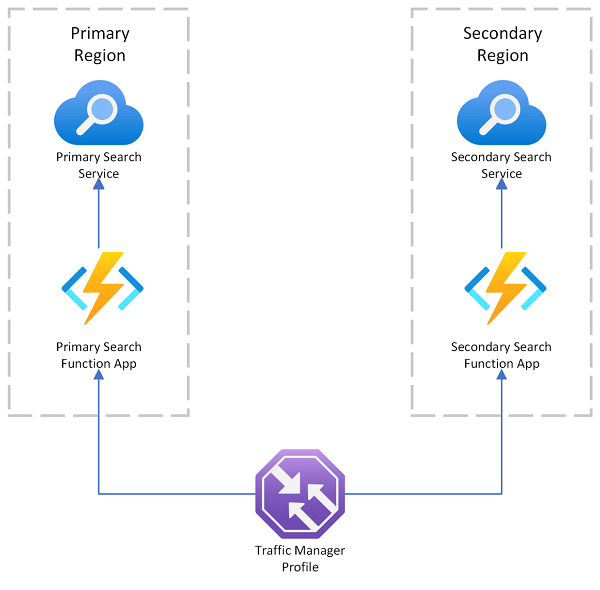
Request failover and redirection
For redundancy at the request level, Azure provides several load-balancing options:
Use Azure Application Gateway to load balance between servers in a region at the application layer.
By default, service endpoints are accessed through a public internet connection. Use Application Gateway if you set up a private endpoint for client connections that originate from within a virtual network.
As you evaluate these load-balancing options, consider the following points:
Azure AI Search is a backend service that accepts indexing and query requests from a client.
By default, service endpoints are accessed through a public internet connection. We recommend Azure Application Gateway for private endpoints that originate from within a virtual network.
Azure AI Search accepts requests addressed to the
<your-search-service-name>.search.windows.netendpoint. If you reach the same endpoint using a different DNS name in the host header, such as a CNAME, the request is rejected.Requests from the client to a search service must be authenticated. To access search operations, the caller must have role-based permissions or provide an API key with the request.