Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This document describes the Offline Security Intelligence Update feature of Microsoft Defender for Endpoint on macOS.
This feature makes it possible for an organization to use a local hosting server (referred to as a mirror server in this document) to update the security intelligence (referred to in this document as definitions or signatures) on macOS endpoints that have limited or no exposure to the internet.
A mirror server is any server in the customer's environment that can connect to the Microsoft cloud to download the signatures. Other macOS endpoints pull the signatures from the mirror server at a predefined interval.
Key benefits
Your security team can control and manage the frequency of signature downloads to the local server and the frequency at which endpoints pull signatures from the local server.
You have an extra layer of protection and control, as the downloaded signatures can be tested on a test device before they're propagated to the entire fleet.
You need less network bandwidth, since only one local server polls the Microsoft cloud to get the latest signatures on behalf of your entire fleet.
Your mirror server can run Windows, Mac, or Linux, and you don't have to install Defender for Endpoint on that server.
You get the most up-to-date antivirus protection, because signatures are always downloaded along with the latest compatible antivirus engine.
Older versions of signatures (n-1) are moved to a backup folder on your mirror server in each iteration. If there's an issue with the latest updates, you can pull the n-1 signature version from the backup folder to your devices.
In the rare event that offline update fails, you can configure a fallback option to get online updates from the Microsoft cloud.
How offline security intelligence update works
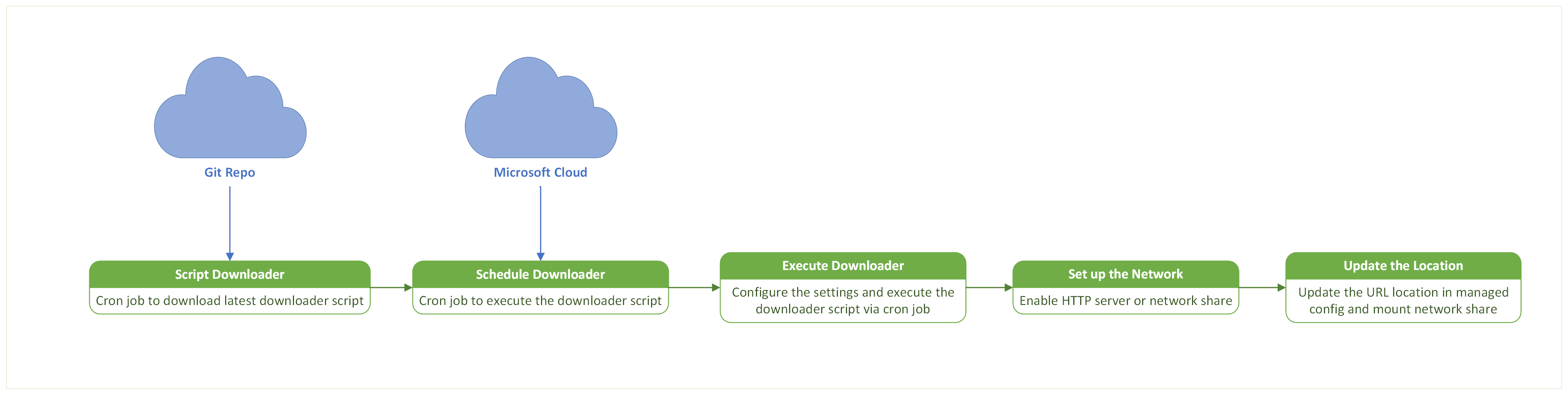
Organizations need to set up a mirror server, which is a local Web/NFS server that's reachable by the Microsoft cloud.
Signatures are downloaded from Microsoft cloud to this mirror server by executing a script using cron job/task scheduler on the local server.
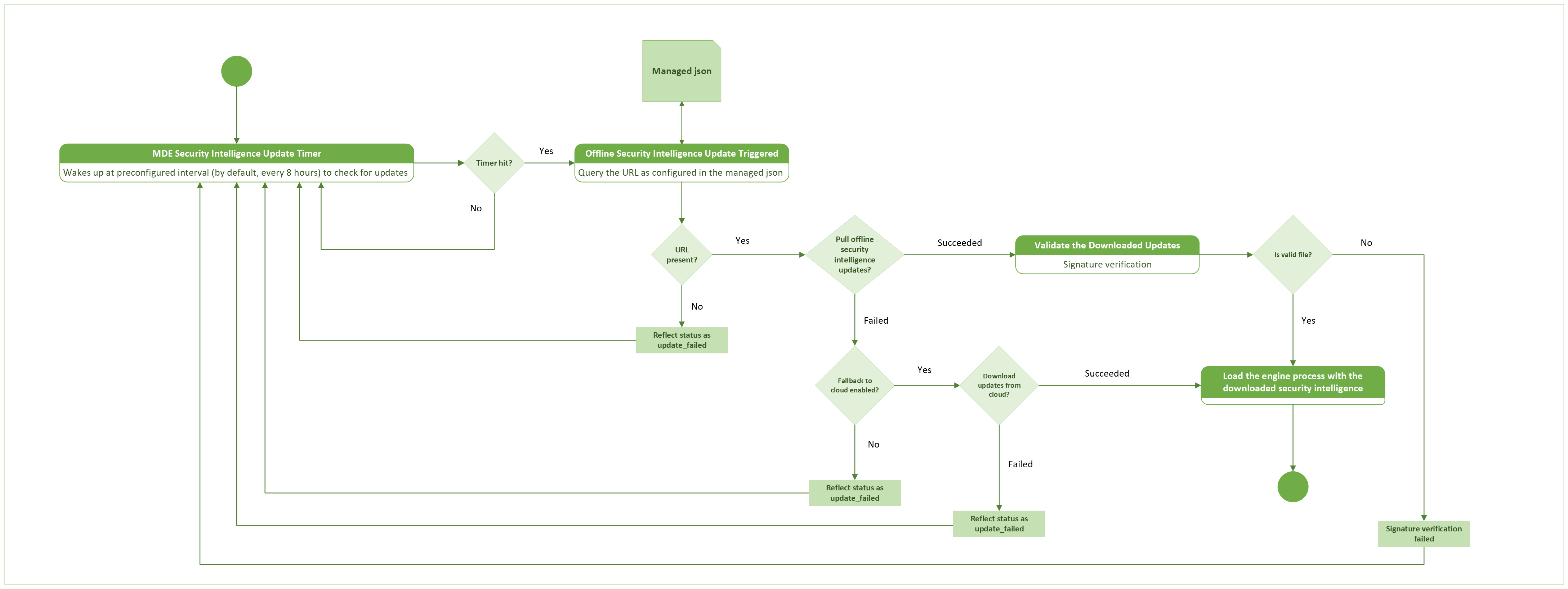
macOS endpoints running Defender for Endpoint pull the downloaded signatures from this mirror server at a user-defined time interval.
Signatures pulled to the macOS endpoints from the local server are first verified before getting loaded into the antivirus engine.
To trigger and configure the update process, update the managed config json file on the macOS endpoints.
The status of the update can be seen on the mdatp CLI.
The process flow for downloading security intelligence updates to the mirror server is illustrated in the following diagram.
The process flow for security intelligence updates on the macOS endpoint is illustrated in the following diagram.
The mirror server can run any of the following operating systems:
- Linux (any flavor)
- Windows (any version)
- Mac (any version)
Prerequisites
Defender for Endpoint version 101.25012.0003 or later must be installed on the macOS endpoints.
The macOS endpoints need to have connectivity to the mirror server.
The macOS endpoint must be running any of the Defender for Endpoint-supported distributions.
The mirror server can be either an HTTP/HTTPS server or a network share server, for example, an NFS server.
The mirror server needs to have access to the following URLs:
https://github.com/microsoft/mdatp-xplat.githttps://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=2144709
The mirror server should support bash or PowerShell.
The following minimum system specifications are required for the mirror server:
CPU Core RAM Free disk Swap 2 cores (Preferred 4 Core) 1 GB Min (Preferred 4 GB) 2 GB System Dependent Note
This configuration might vary depending on the number of requests that are served and the load each server must process.
Configure the mirror server
Note
Management and ownership of the mirror server lies solely with the customer, as it resides in the customer's private environment.
Any HTTP server can be used as a mirror server. The mirror server doesn't need to have Defender for Endpoint installed.
While management and ownership of the mirror server lies solely with the customer, this section presents two sample Bash scripts that demonstrate how to use Python 3 and Caddy to set up a basic HTTP file server on macOS. These scripts are given for purposes of illustration only and should be adapted to your own specific needs and environment.
python_http_server.sh: Uses Python 3's built-in HTTP server module to serve files from a specified directory.caddy_http_server.sh: Installs and configures the Caddy web server to serve files from a specified directory.
To check that the service is set up correctly after you've set up the server, navigate to "https://localhost:8080".
For production or advanced use cases, refer to the official documentation for each server:
Always review and adapt scripts to your environment and security requirements.
Sample script: Setting up a basic HTTP file server on macOS using Python 3
#!/bin/bash
# python_http_server.sh
# Starts a simple HTTP server using Python 3
# Check for Python 3
if ! command -v python3 &> /dev/null; then
echo "Python 3 is not installed. Please install it first."
exit 1
fi
PORT=8080
FOLDER="."
if [ ! -z "$1" ]; then
PORT=$1
fi
if [ ! -z "$2" ]; then
FOLDER=$2
fi
echo "Starting Python HTTP server on port $PORT (localhost only), serving folder: $FOLDER..."
python3 -m http.server "$PORT" --bind 127.0.0.1 --directory "$FOLDER"
Sample script: Setting up a basic HTTP file server on macOS using using Caddy
#!/bin/bash
# caddy_http_server.sh
# Installs and configures Caddy HTTP server on macOS
PORT=8080
FOLDER="."
if [ ! -z "$1" ]; then
PORT=$1
fi
if [ ! -z "$2" ]; then
FOLDER=$2
fi
check_homebrew() {
if ! command -v brew &> /dev/null; then
echo "Homebrew is required to install Caddy."
read -p "Would you like to install Homebrew? (y/n): " install_brew
if [[ "$install_brew" =~ ^[Yy]$ ]]; then
echo "Installing Homebrew..."
/bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/HEAD/install.sh)"
export PATH="/opt/homebrew/bin:$PATH"
else
echo "Please install Caddy manually and restart this script."
exit 1
fi
fi
}
install_caddy() {
if ! brew list caddy &> /dev/null; then
echo "Installing Caddy via Homebrew..."
brew install caddy
else
echo "Caddy is already installed."
fi
}
# Check for Caddy
if ! command -v caddy &> /dev/null; then
echo "Caddy is not installed."
check_homebrew
install_caddy
else
echo "Caddy is already installed."
fi
# Create a simple Caddyfile
cat <<EOL > Caddyfile
localhost:${PORT} {
root * ${FOLDER}
file_server browse
}
EOL
echo "Caddyfile created. Starting Caddy server on port $PORT..."
caddy run --config ./Caddyfile
Get the offline security intelligence downloader script
Microsoft hosts an offline security intelligence downloader script in the following GitHub repo: https://github.com/microsoft/mdatp-xplat.
Perform the following steps to get the downloader script:
Option 1: Clone the repo (preferred)
Install git on the mirror server.
Navigate to the directory where you want to clone the repo.
Run the command: git clone https://github.com/microsoft/mdatp-xplat.git
Option 2: Download the zip file
Download the zip file of the repo: https://github.com/microsoft/mdatp-xplat/archive/refs/heads/master.zip.
Copy the zip file to the folder where you want to keep the script.
Extract the zipped folder.
Note
Schedule a cron job or a launchd job to keep the repo/downloaded zip file updated to the latest version at regular intervals.
After cloning the repo or downloading the zipped file, the local directory structure should be as follows:
user@vm:~/mdatp-xplat$ tree linux/definition_downloader/
linux/definition_downloader/
├── README.md
├── settings.json
├── settings.ps1
├── xplat_offline_updates_download.ps1
└── xplat_offline_updates_download.sh
0 directories, 5 files
Note
Go through the README.md file to understand in detail about how to use the script.
The settings.json file consists of a few variables that the user can configure to determine the output of the script execution.
| Field Name | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
downloadFolder |
string | Maps to the ___location where the script downloads the files to. |
downloadLinuxUpdates |
bool | When set to true, the script downloads the Linux specific updates to the downloadFolder. |
logFilePath |
string | Sets up the diagnostic logs at a given folder. This file can be shared with Microsoft for debugging the script if there are any issues. |
downloadMacUpdates |
bool | The script downloads the Mac-specific updates to the downloadFolder. |
downloadPreviewUpdates |
bool | Downloads the preview version of the updates available for the specific OS. |
backupPreviousUpdates |
bool | Allows the script to copy the previous update in the _back folder, and new updates are downloaded to downloadFolder. |
Execute the offline security intelligence downloader script
To manually execute the downloader script, configure the parameters in the settings.json file as per the description in the previous section, and use one of the following commands based on the OS of the mirror server:
Bash:
./xplat_offline_updates_download.sh
PowerShell:
./xplat_offline_updates_download.ps1
Note
Schedule a cron job or a launchd job to execute this script to download the latest security intelligence updates to the mirror server at regular intervals.
Host the offline security intelligence updates on the mirror server
Once the script is executed, the latest signatures get downloaded to the folder configured in the settings.json file (updates.zip).
Once the signatures zip is downloaded, the mirror server can be used to host it. The mirror server can be hosted using any of the HTTP/HTTPS/network share servers.
Once hosted, copy the absolute path of the hosted server (up to but not including the arch_* directory).
For example, if the script is executed with downloadFolder=/tmp/wdav-update, and the HTTP server (www.example.server.com:8000) is hosting the /tmp/wdav-update path, the corresponding URI is: www.example.server.com:8000/mac/production/.
We can also use the absolute path of directory (local/remote mount point) like /tmp/wdav-update/mac/production.
Once the mirror server is set up, we need to propagate this URL to the Mac endpoints as the offlineDefinitionUpdateUrl in the Managed Configuration as described in the next section.
Configure the endpoints
Use the following sample mdatp_managed.json file and update the parameters as per the configuration, then copy the file to the ___location /etc/opt/microsoft/mdatp/managed/mdatp_managed.json.
{
"cloudService": {
"automaticDefinitionUpdateEnabled": true,
"definitionUpdatesInterval": 1202
},
"antivirusEngine": {
"offlineDefinitionUpdateUrl": "http://172.22.199.67:8000/mac/production/",
"offlineDefintionUpdateFallbackToCloud":false,
"offlineDefinitionUpdate": "enabled"
},
"features": {
"offlineDefinitionUpdateVerifySig": "enabled"
}
}
| Field Name | Values | Comments |
|---|---|---|
automaticDefinitionUpdateEnabled |
true/false |
Determines the behavior of Defender for Endpoint attempting to perform updates automatically, is turned on or off respectively. |
definitionUpdatesInterval |
numeric | Time of interval between each automatic update of signatures (in seconds). |
offlineDefinitionUpdateUrl |
string | URL value generated as part of the mirror server setup. This can be either in terms of the remote server URL or a directory (local/remote mount point). |
offlineDefinitionUpdate |
enabled/disabled |
When set to enabled, the "offline security intelligence update" feature is enabled, and vice versa. |
offlineDefinitionUpdateFallbackToCloud |
true/false |
Determine the Defender for Endpoint security intelligence update approach when "offline mirror server" fails to serve the update request. If set to true, the update is retried via the Microsoft cloud when "offline security intelligence update" failed; else, vice versa. |
offlineDefinitionUpdateVerifySig |
enabled/disabled |
When set to enabled, downloaded definitions are verified on the endpoints; else, vice versa. |
Verify the configuration
To test if the settings are applied correctly on the macOS endpoints, run the following command:
mdatp health --details definitions
A sample output would look like the following code snippet:
user@vm:~$ mdatp health --details definitions
automatic_definition_update_enabled : true [managed]
definitions_updated : Mar 14, 2024 at 12:13:17 PM
definitions_updated_minutes_ago : 2
definitions_version : "1.407.417.0"
definitions_status : "up_to_date"
definitions_update_source_uri : "https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=2144709"
definitions_update_fail_reason : ""
offline_definition_url_configured : "http://172.XX.XXX.XX:8000/mac/production/" [managed]
offline_definition_update : "enabled" [managed]
offline_definition_update_verify_sig : "enabled"
offline_definition_update_fallback_to_cloud : false[managed]
Trigger the offline security intelligence updates
Automatic update
If the fields
automaticDefinitionUpdateEnabledandoffline_definition_updatein the managed json are set totrue, then the "offline security intelligence updates" are triggered automatically at periodic intervals.By default, this periodic interval is 8 hours. It can be configured by setting the
definitionUpdatesIntervalparameter in the managed json.Manual update
To trigger the "offline security intelligence update" manually to download the signatures from the mirror server on the Mac endpoints, run the following command:
mdatp definitions update
Check update status
After triggering the "offline security intelligence update" by either the automatic or manual method, verify that the update was successful by running the command: mdatp health --details --definitions.
Verify the following fields:
user@vm:~$ mdatp health --details definitions
...
definitions_status : "up_to_date"
...
definitions_update_fail_reason : ""
...
Common troubleshooting steps
Check the status of the "offline security intelligence update" feature by using the following command:
mdatp health --details definitionsThis command provides a user-friendly message in the definitions_update_fail_reason section.
Check if
offline_definition_updateandoffline_definition_update_verify_sigare enabled.Check if
definitions_update_source_uriis equal tooffline_definition_url_configured.definitions_update_source_uriis the source from where the signatures were downloaded.offline_definition_url_configuredis the source from where signatures should be downloaded, the one mentioned in the managed config file.
Try performing the connectivity test to check if mirror server is reachable from the host:
mdatp connectivity testTry to trigger a manual update using the following command:
mdatp definitions update