Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Applies to: ✅ SQL analytics endpoint and Warehouse in Microsoft Fabric
Fabric Data Warehouse is an enterprise scale relational warehouse on a data lake foundation.
- The ideal use cases for Fabric Data Warehouse are star or snowflake schemas, curated corporate data marts, governed semantic models for business intelligence.
- Fabric Data Warehouse data, like all Fabric data, is stored in Delta tables, which are Parquet data files with a file-based transaction log. Built on the Fabric open data format, a warehouse allows sharing and collaboration between data engineers and business users without compromising security or governance.
- Fabric Data Warehouse is primarily developed with T-SQL, and shares a large surface area based on the SQL Database Engine, with full multi-table ACID transaction support, materialized views, functions, and stored procedures.
- Bulk loading of Fabric Data Warehouse can be accomplished via T-SQL and TDS connections, or via Spark, with data bulk written directly to the Delta tables.
- The easy-to-use SaaS experience is also tightly integrated with Power BI for easy analysis and reporting.
Data warehouse customers benefit from:
- Cross database queries can use multiple data sources for fast insights with zero data duplication.
- Easily ingest, load and transform data at scale through Pipelines, Dataflows, cross database query or the COPY INTO command.
- Autonomous workload management with industry-leading distributed query processing engine means no knobs to turn to achieve best in class performance.
- Scale near instantaneously to meet business demands. Storage and compute are separated.
- Data is automatically replicated to OneLake Files for external access.
- Built for any skill level, from the citizen developer to DBA or data engineer.
Data warehousing items
Fabric Data Warehouse is not a traditional enterprise data warehouse, it's a lake warehouse that supports two distinct warehousing items: the Fabric warehouse item and the SQL analytics endpoint item. Both are purpose-built to meet customers' business needs while providing best in class performance, minimizing costs, and reduced administrative overhead.
Fabric Data Warehouse
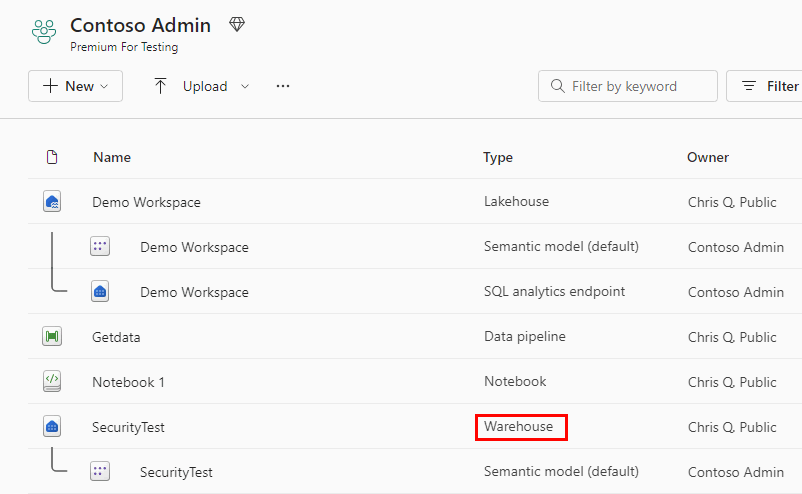
In a Microsoft Fabric workspace, a Fabric warehouse is labeled as Warehouse in the Type column. When you need the full power and transactional capabilities (DDL and DML query support) of a data warehouse, this is the fast and simple solution for you.
The warehouse can be populated by any one of the supported data ingestion methods such as COPY INTO, Pipelines, Dataflows, or cross database ingestion options such as CREATE TABLE AS SELECT (CTAS), INSERT..SELECT, or SELECT INTO.
To get started with the Warehouse, see:
SQL analytics endpoint of the Lakehouse
In a Microsoft Fabric workspace, each Lakehouse has an autogenerated "SQL analytics endpoint" which can be used to transition from the "Lake" view of the Lakehouse (which supports data engineering and Apache Spark) to the "SQL" view of the same Lakehouse to create views, functions, stored procedures, and apply SQL security.
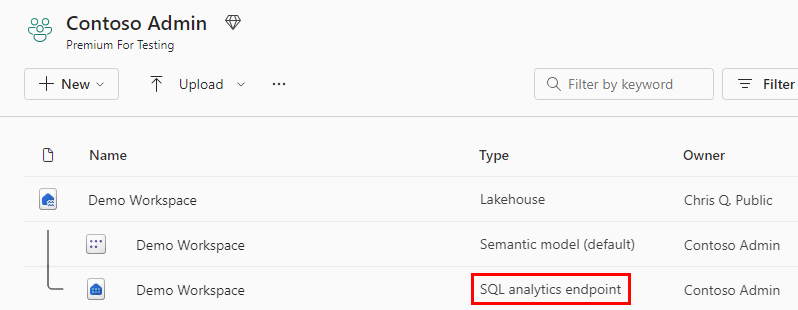
Using similar technology, a warehouse, a SQL database, and Fabric OneLake all automatically provision a SQL analytics endpoint when created.
With the SQL analytics endpoint, T-SQL commands can define and query data objects but not manipulate or modify the data. You can perform the following actions in the SQL analytics endpoint:
- Query the tables that reference data in your Delta Lake folders in the lake.
- Create views, inline TVFs, and procedures to encapsulate your semantics and business logic in T-SQL.
- Manage permissions on the objects. For more about security in the SQL anlaytics endpoint, see OneLake security for SQL analytics endpoints.
To get started with the SQL analytics endpoint, see:
- Better together: the lakehouse and warehouse in Microsoft Fabric
- SQL analytics endpoint performance considerations
- Query the SQL analytics endpoint or Warehouse in Microsoft Fabric
Warehouse or lakehouse
When deciding between using a warehouse or a lakehouse, it's important to consider the specific needs and context of your data management and analytics requirements.
Choose a data warehouse when you need an enterprise-scale solution with open standard format, no knobs performance, and minimal setup. Best suited for semi-structured and structured data formats, the data warehouse is suitable for both beginner and experienced data professionals, offering simple and intuitive experiences.
Choose a lakehouse when you need a large repository of highly unstructured data from heterogeneous sources and want to use Spark as your primary development tool. Acting as a 'lightweight' data warehouse, you always have the option to use the SQL analytics endpoint and T-SQL tools to deliver reporting and data intelligence scenarios in your lakehouse.
You always have the opportunity to add one or the other at a later point should your business needs change and regardless of where you start, both the warehouse and the lakehouse use the same powerful SQL engine for all T-SQL queries.
For more detailed decision guidance, see Microsoft Fabric decision guide: Choose between Warehouse and Lakehouse.
Migration
Use the Fabric Migration Assistant for Data Warehouse to migrate from Azure Synapse Analytics, SQL Server, and other SQL Database Engine platforms. Review Migration planning and Migration methods for Azure Synapse Analytics dedicated SQL pools to Fabric Data Warehouse.
For migration guidance across Microsoft Fabric, review the tools and links in Microsoft Fabric migration overview.