Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
APPLIES TO: Developer | Basic | Basic v2 | Standard | Standard v2 | Premium | Premium v2
This article shows how to use API Management to expose and govern an existing remote Model Context Protocol (MCP) server - a tool server hosted outside of API Management. Expose and govern the server's tools through API Management so that MCP clients can call them by using the MCP protocol.
Example scenarios include:
- Proxy LangChain or LangServe tool servers through API Management with per-server authentication and rate limits.
- Securely expose Azure Logic Apps–based tools to copilots by using IP filtering and OAuth.
- Centralize MCP server tools from Azure Functions and open-source runtimes into Azure API Center.
- Enable GitHub Copilot, Claude by Anthropic, or ChatGPT to interact securely with tools across your enterprise.
API Management also supports MCP servers natively exposed in API Management from managed REST APIs. For more information, see Expose a REST API as an MCP server.
Learn more about:
Limitations
The external MCP server must conform to MCP version
2025-06-18or later. The server can support:- Either no authorization, or authorization protocols that comply with the following standards: https://modelcontextprotocol.io/specification/2025-06-18/basic/authorization#standards-compliance.
- Streamable HTTP or SSE transport types.
API Management currently supports MCP server tools, but it doesn't support MCP resources or prompts.
API Management currently doesn't support MCP server capabilities in workspaces.
Prerequisites
If you don't already have an API Management instance, complete the following quickstart: Create an Azure API Management instance. The instance must be in one of the service tiers that supports MCP servers.
Access to an external MCP-compatible server (for example, hosted in Azure Logic Apps, Azure Functions, LangServe, or other platforms).
Appropriate credentials to the MCP server (such as OAuth 2.0 client credentials or API keys, depending on the server) for secure access.
If you enable diagnostic logging through Application Insights or Azure Monitor at the global scope (all APIs) for your API Management instance, set the Number of payload bytes to log setting for Frontend Response to 0. This setting prevents unintended logging of response bodies across all APIs and helps ensure proper functioning of MCP servers. To log payloads selectively for specific APIs, configure the setting individually at the API scope, allowing targeted control over response logging.
To test the MCP server, use Visual Studio Code with access to GitHub Copilot or a tool such as MCP Inspector.
Expose an existing MCP server
Follow these steps to expose an existing MCP server in API Management:
- In the Azure portal, go to your API Management instance.
- In the left-hand menu, under APIs, select MCP servers > + Create MCP server.
- Select Expose an existing MCP server.
- In Backend MCP server:
- Enter the existing MCP server base URL. For example,
https://learn.microsoft.com/api/mcpfor the Microsoft Learn MCP server. - In Transport type, Streamable HTTP is selected by default.
- Enter the existing MCP server base URL. For example,
- In New MCP server:
- Enter a Name for the MCP server in API Management.
- In Base path, enter a route prefix for tools. For example,
mytools. - Optionally, enter a Description for the MCP server.
- Select Create.

- The MCP server is created and the remote server's operations are exposed as tools.
- The MCP server is listed in the MCP Servers pane. The Server URL column shows the MCP server URL to call for testing or within a client application.
Important
Currently, API Management doesn't display tools from the existing MCP server. You must register and configure all tools on the existing remote MCP server.
Configure policies for the MCP server
Configure one or more API Management policies to help manage the MCP server. The policies apply to all API operations exposed as tools in the MCP server. Use these policies to control access, authentication, and other aspects of the tools.
Learn more about configuring policies:
- Policies in API Management
- Transform and protect your API
- Set and edit policies
- Secure access to MCP server
Caution
Don't access the response body by using the context.Response.Body variable within MCP server policies. Doing so triggers response buffering, which interferes with the streaming behavior required by MCP servers and might cause them to malfunction.
To configure policies for the MCP server, follow these steps:
In the Azure portal, go to your API Management instance.
In the left-hand menu, under APIs, select MCP Servers.
Select an MCP server from the list.
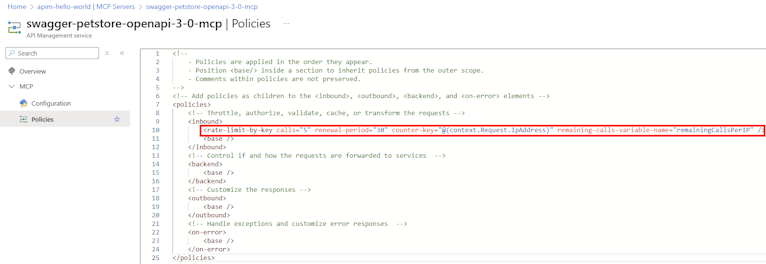
In the left menu, under MCP, select Policies.
In the policy editor, add or edit the policies you want to apply to the MCP server's tools. Define the policies in XML format.
For example, you can add a policy to limit calls to the MCP server's tools (in this example, one call per 60 seconds per MCP session).
<!-- Rate limit tool calls by Mcp-Session-Id header --> <set-variable name="body" value="@(context.Request.Body.As<string>(preserveContent: true))" /> <choose> <when condition="@( Newtonsoft.Json.Linq.JObject.Parse((string)context.Variables["body"])["method"] != null && Newtonsoft.Json.Linq.JObject.Parse((string)context.Variables["body"])["method"].ToString() == "tools/call" )"> <rate-limit-by-key calls="1" renewal-period="60" counter-key="@( context.Request.Headers.GetValueOrDefault("Mcp-Session-Id", "unknown") )" /> </when> </choose>
Note
API Management evaluates policies configured at the global (all APIs) scope before it evaluates policies at the MCP server scope.
Validate and use the MCP server
Use a compliant LLM agent (such as GitHub Copilot, Semantic Kernel, or Copilot Studio) or a test client (such as curl) to call the API Management-hosted MCP endpoint. Ensure that the request includes appropriate headers or tokens, and confirm successful routing and response from the MCP server.
Tip
If you use the MCP Inspector to test an MCP server managed by API Management, use version 0.9.0.
Add the MCP server in Visual Studio Code
In Visual Studio Code, use GitHub Copilot chat in agent mode to add the MCP server and use the tools. For background about MCP servers in Visual Studio Code, see Use MCP Servers in VS Code.
To add the MCP server in Visual Studio Code:
Use the MCP: Add Server command from the Command Palette.
When prompted, select the server type: HTTP (HTTP or Server Sent Events).
Enter the Server URL of the MCP server in API Management. For example,
https://<apim-service-name>.azure-api.net/<api-name>-mcp/mcpfor the MCP endpoint.Enter a Server ID of your choice.
Select whether to save the configuration to your workspace settings or user settings.
Workspace settings - The server configuration is saved to a
.vscode/mcp.jsonfile only available in the current workspace.User settings - The server configuration is added to your global
settings.jsonfile and is available in all workspaces. The configuration looks similar to the following:
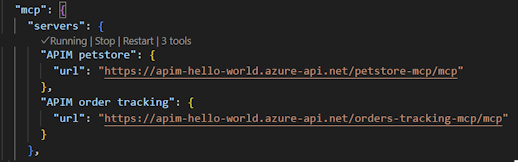
Add fields to the JSON configuration for settings such as authentication header. The following example shows the configuration for an API Management subscription key passed in a header as in input value. Learn more about the configuration format

Use tools in agent mode
After adding an MCP server in Visual Studio Code, you can use tools in agent mode.
In GitHub Copilot chat, select Agent mode and select the Tools button to see available tools.

Select one or more tools from the MCP server to be available in the chat.
Enter a prompt in the chat to invoke the tool. For example, if you selected a tool to get information about an order, you can ask the agent about an order.
Get information for order 2Select Continue to see the results. The agent uses the tool to call the MCP server and returns the results in the chat.

Troubleshooting and known issues
| Problem | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
401 Unauthorized error from backend |
Authorization header not forwarded | If necessary, use set-header policy to manually attach token |
| API call works in API Management but fails in agent | Incorrect base URL or missing token | Double-check security policies and endpoint |
| MCP server streaming fails when diagnostic logs are enabled | Logging of response body or accessing response body through policy interferes with MCP transport | Disable response body logging at the All APIs scope - see Prerequisites |